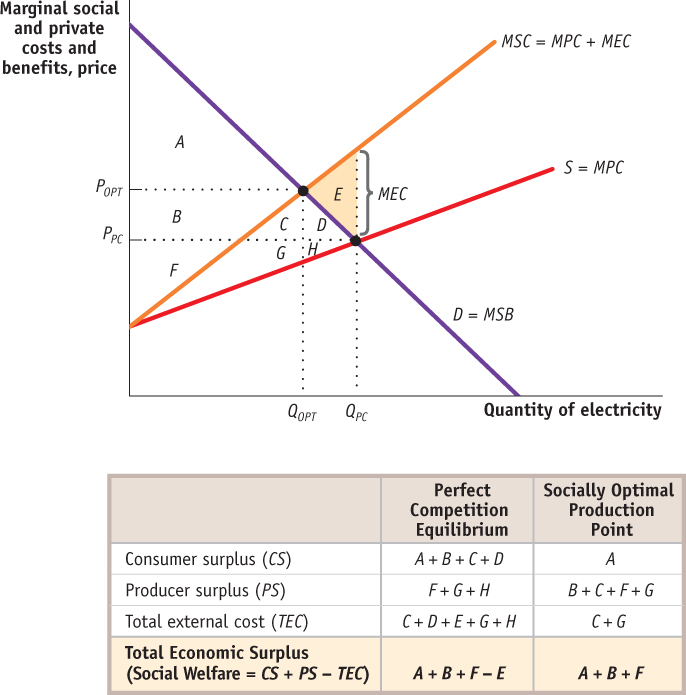
Figure16-3Perfect Competition with Externalities When externalities are created either in production or consumption of a good or service, a perfectly competitive market is inefficient resulting in a deadweight loss. The market for electricity is plagued by a negative externality as the production of electricity often creates significant amounts of harmful pollution. The competitive equilibrium occurs at the intersection between the supply and demand curves. The socially optimal level of output occurs where the marginal social benefit curve intersects the marginal social cost curve. Since the market ignores the negative externality, perfect competition results in too much electricity being produced (and too much pollution) and in electricity being sold at a price that is too low.