3.3 The Supply Curve
Some parts of the world are especially well-
The quantity supplied is the actual amount of a good or service people are willing and able to sell at some specific price.
So just as the quantity of cotton that consumers want to buy depends on the price they have to pay, the quantity that producers are willing and able to produce and sell—
The Supply Schedule and the Supply Curve
The table in Figure 3-6 shows how the quantity of cotton made available varies with the price—
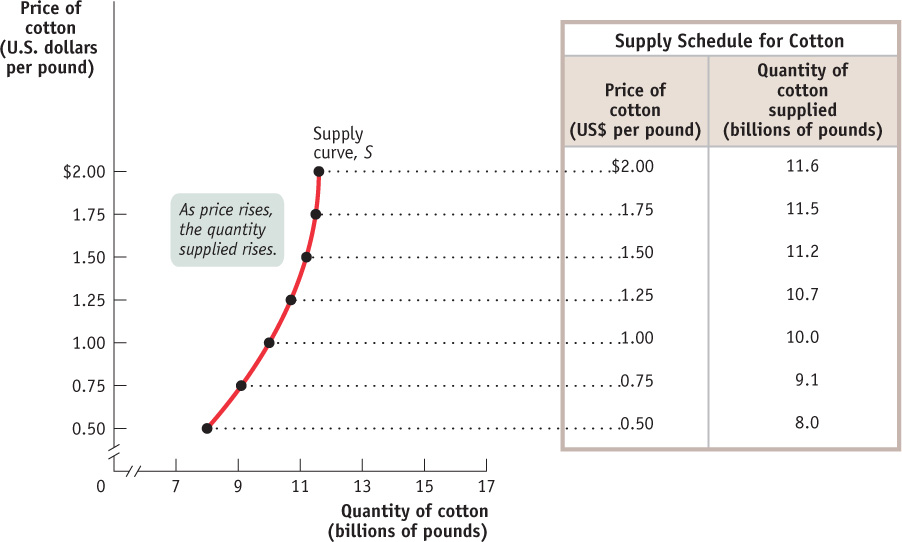
A supply schedule shows how much of a good or service would be supplied at different prices.
A supply schedule works the same way as the demand schedule shown in Figure 3-1: in this case, the table shows the number of pounds of cotton farmers are willing to sell at different prices. At a price of $0.50 per pound, farmers are willing to sell only 8 billion pounds of cotton per year. At $0.75 per pound, they’re willing to sell 9.1 billion pounds. At $1, they’re willing to sell 10 billion pounds, and so on.
A supply curve shows the relationship between quantity supplied and price.
In the same way that a demand schedule can be represented graphically by a demand curve, a supply schedule can be represented by a supply curve, as shown in Figure 3-6. Each point on the curve represents an entry from the table.
Suppose that the price of cotton rises from $1 to $1.25; we can see that the quantity of cotton farmers are willing to sell rises from 10 billion to 10.7 billion pounds. This is the normal situation for a supply curve, that a higher price leads to a higher quantity supplied. So just as demand curves normally slope downward, supply curves normally slope upward: the higher the price being offered, the more of any good or service producers will be willing to sell (and vice versa).
Shifts of the Supply Curve
Until recently, cotton remained relatively cheap over the past several decades. One reason is that the amount of land cultivated for cotton worldwide expanded more than 35% from 1945 to 2007. However, the major factor accounting for cotton’s relative cheapness was advances in the production technology, with output per hectare more than quadrupling from 1945 to 2007. Figure 3-7 illustrates these events in terms of the supply schedule and the supply curve for cotton.
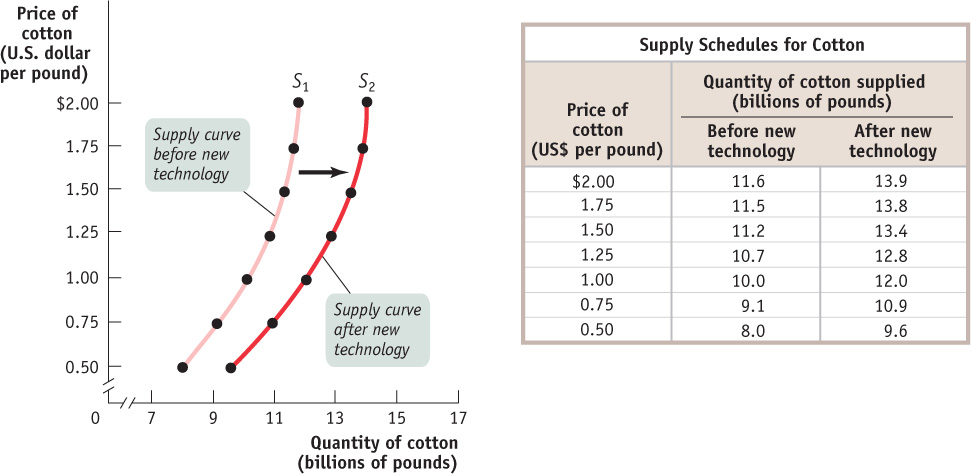
A shift of the supply curve is a change in the quantity supplied of a good or service at any given price. It is represented by the change (shift) of the original supply curve to a new position, denoted by a new supply curve.
The table in Figure 3-7 shows two supply schedules. The schedule before improved cotton-
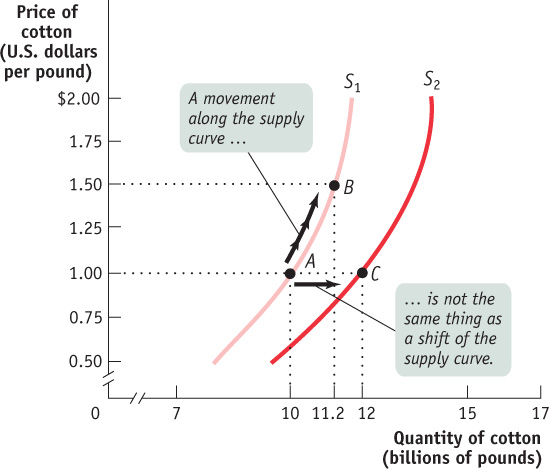
A movement along the supply curve is a change in the quantity supplied of a good arising from a change in the good’s price.
As in the analysis of demand, it’s crucial to draw a distinction between such shifts of the supply curve and movements along the supply curve—changes in the quantity supplied arising from a change in price (all other things equal). We can see this difference in Figure 3-8. The movement from point A to point B is a movement along the supply curve: the quantity supplied rises along S1 due to a rise in price. Here, a rise in price from $1 to $1.50 leads to a rise in the quantity supplied from 10 billion to 11.2 billion pounds of cotton. But the quantity supplied can also rise when the price is unchanged if there is an increase in supply—
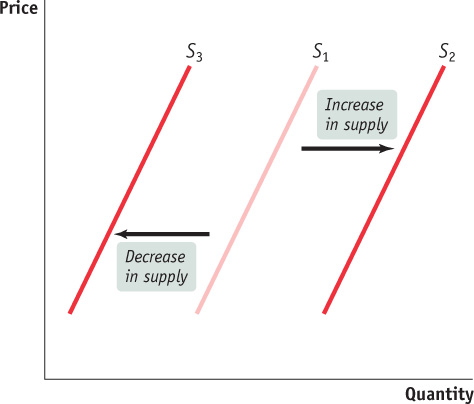
Understanding Shifts of the Supply Curve
Figure 3-9 illustrates the two basic ways in which supply curves can shift. When economists talk about an “increase in supply,” they mean a rightward shift of the supply curve: at any given price, producers supply a larger quantity of the good than before. This is shown in Figure 3-9 by the rightward shift of the original supply curve S1 to S2. And when economists talk about a “decrease in supply,” they mean a leftward shift of the supply curve: at any given price, producers supply a smaller quantity of the good than before. This is represented by the leftward shift of S1 to S3.
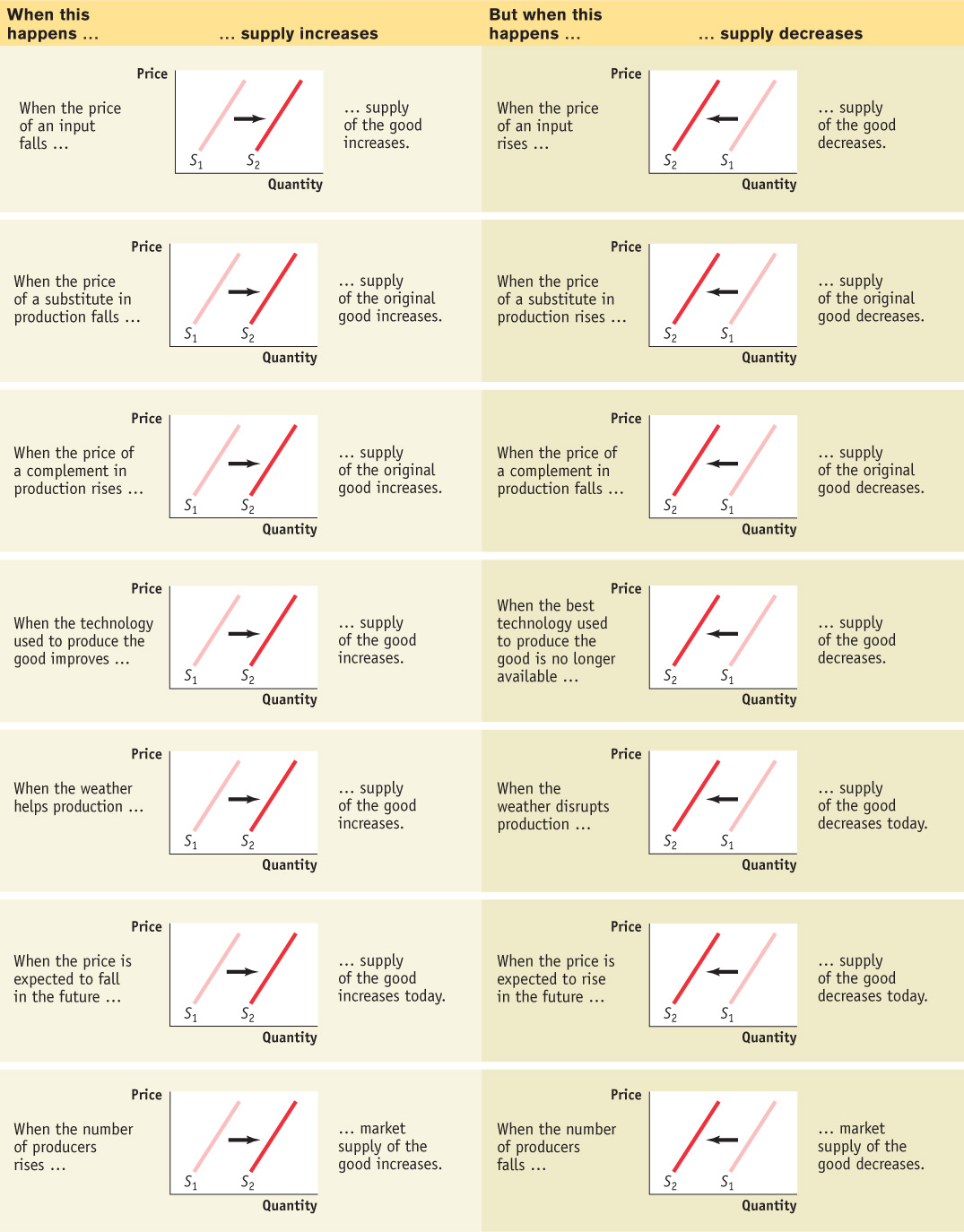
Economists believe that shifts of the supply curve for a good or service are mainly the result of six factors (though, as in the case of demand, there are other possible causes):
Changes in input prices
Changes in the prices of related goods or services
Changes in technology
Changes in weather
Changes in expectations
Changes in the number of producers
Changes in Input Prices To produce output, you need inputs. For example, to make vanilla ice cream, you need vanilla beans, cream, sugar, and so on. An input is any good or service that is used to produce another good or service. Inputs, like outputs, have prices. And an increase in the price of an input makes the production of the final good more costly for those who produce and sell it. So producers are less willing to supply the final good at any given price, and the supply curve shifts to the left. For example, fuel is a major cost for airlines. When oil prices surged in 2007–2008, airlines began cutting back on their flight schedules and some, like Canada’s Zoom Airlines, went out of business. Similarly, a fall in the price of an input makes the production of the final good less costly for sellers. They are more willing to supply the good at any given price because they are making more profit than before, and the supply curve shifts to the right.
An input is a good or service that is used to produce another good or service.
Changes in the Prices of Related Goods or Services A single producer often produces a mix of goods rather than a single product. For example, an oil refinery produces gasoline from crude oil, but it also produces heating oil and other products from the same raw material. When a producer sells several products, the quantity of any one good it is willing to supply at any given price depends on the prices of its other co-produced goods.
This effect can run in either direction. An oil refiner will supply less gasoline at any given price when the price of heating oil rises, shifting the supply curve for gasoline to the left. But it will supply more gasoline at any given price when the price of heating oil falls, shifting the supply curve for gasoline to the right. This means that gasoline and other co-produced oil products are substitutes in production for refiners.
In contrast, due to the nature of the production process, other goods can be complements in production. For example, producers of crude oil—oil-well drillers—often find that oil wells also produce natural gas as a by-product of oil extraction. The higher the price at which a driller can sell its natural gas, the more oil wells it will drill and the more oil it will supply at any given price for oil. As a result, natural gas is a complement in production for crude oil.
Changes in Technology When economists talk about “technology,” they don’t necessarily mean high technology—they mean all the methods people can use to turn inputs into useful goods and services. In that sense, the whole complex sequence of activities that turn cotton from Pakistan into the pair of jeans hanging in your closet is technology.
Improvements in technology enable producers to spend less on inputs yet still produce the same output. When a better technology becomes available, reducing the cost of production, supply increases, and the supply curve shifts to the right. As we have already mentioned, improved technology enabled farmers worldwide to more than quadruple cotton output per hectare planted over the past several decades. Improved technology is the main reason that, until recently, cotton remained relatively cheap even as worldwide demand grew.
Changes in Weather A change in growing conditions or weather can also affect the supply of a good. For example, when a drought hits the Prairies, the growing conditions for wheat and other grain products becomes unfavourable. As a result, the supply of grain products decreases. Similarly, flooding in Alberta may result in a reduction in supply of grain or other goods due to the disruptions it causes.
Changes in Expectations Just as changes in expectations can shift the demand curve, they can also shift the supply curve. When suppliers have some choice about when they put their good up for sale, changes in the expected future price of the good can lead a supplier to supply less or more of the good today.
For example, consider the fact that gasoline and other oil products are often stored for significant periods of time at oil refineries before being sold to consumers. In fact, storage is normally part of producers’ business strategy. Knowing that the demand for gasoline peaks in the summer, oil refiners normally store some of their gasoline produced during the spring for summer sale. Similarly, knowing that the demand for heating oil peaks in the winter, they normally store some of their heating oil produced during the fall for winter sale. In each case, there’s a decision to be made between selling the product now versus storing it for later sale. Which choice a producer makes depends on a comparison of the current price versus the expected future price. This example illustrates how changes in expectations can alter supply. An increase in the anticipated future price of a good or service reduces supply today, a leftward shift of the supply curve. But a fall in the anticipated future price increases supply today, a rightward shift of the supply curve.
Changes in the Number of Producers Just as changes in the number of consumers affect the (market) demand curve, changes in the number of producers affect the (market) supply curve. Let’s examine the individual supply curve, by looking at panel (a) in Figure 3-10. The individual supply curve shows the relationship between quantity supplied and price for an individual producer. For example, suppose that Mr. Silva is a Brazilian cotton farmer and that panel (a) of Figure 3-10 shows how many pounds of cotton he will supply per year at any given price. Then SSilva is his individual supply curve.
An individual supply curve illustrates the relationship between quantity supplied and price for an individual producer.
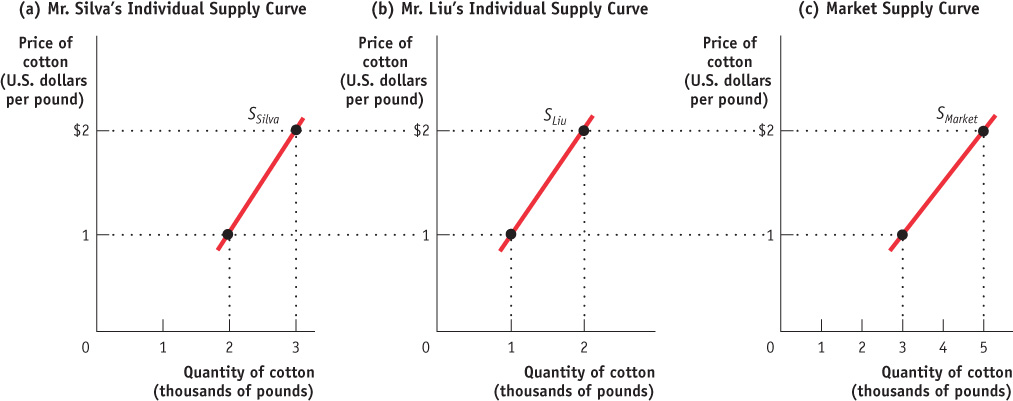
The market supply curve shows how the combined total quantity supplied by all individual producers in the market depends on the market price of that good. Just as the market demand curve is the horizontal sum of the individual demand curves of all consumers, the market supply curve is the horizontal sum of the individual supply curves of all producers. Assume for a moment that there are only two producers of cotton, Mr. Silva and Mr. Liu, a Chinese cotton farmer. Mr. Liu’s individual supply curve is shown in panel (b). Panel (c) shows the market supply curve. At any given price, the quantity supplied to the market is the sum of the quantities supplied by Mr. Silva and Mr. Liu. For example, at a price of $2 per pound, Mr. Silva supplies 3000 pounds of cotton per year and Mr. Liu supplies 2000 pounds per year, making the quantity supplied to the market 5000 pounds.
Clearly, the quantity supplied to the market at any given price is larger with Mr. Liu present than it would be if Mr. Silva were the only supplier. The quantity supplied at a given price would be even larger if we added a third producer, then a fourth, and so on. So an increase in the number of producers leads to an increase in supply and a rightward shift of the supply curve.
For a review of the factors that shift supply, see Table 3-2.
ONLY CREATURES SMALL AND PAMPERED
During the 1970s, British television featured a popular show titled All Creatures Great and Small. It chronicled the real life of James Herriot, a country veterinarian who tended to cows, pigs, sheep, horses, and the occasional house pet, often under arduous conditions, in rural England during the 1930s. The show made it clear that in those days the local vet was a critical member of farming communities, saving valuable farm animals and helping farmers survive financially. And it was also clear that Mr. Herriot considered his life’s work well spent.

But that was then and this is now. Canada and the United States have experienced a severe decline in the number of farm vets over the past two decades. The source of the problem is competition. As the number of household pets has increased and the incomes of pet owners have grown, the demand for pet vets has increased sharply. As a result, vets are being drawn away from the business of caring for farm animals into the more lucrative business of caring for pets. As one American vet stated, she began her career caring for farm animals but changed her mind after “doing a C-section on a cow and it’s 50 bucks. Do a C-section on a Chihuahua and you get $300. It’s the money. I hate to say that.” Add to this the relatively long hours and greater need for travel required of farm vets and it’s easy to see why this choice less appealing than being a pet vet in an urban centre.
How can we translate this into supply and demand curves? Farm veterinary services and pet veterinary services are like gasoline and fuel oil: they’re related goods that are substitutes in production. A vet typically specializes in one type of practice or the other, and that decision often depends on the going price for the service. The growing pet population in North America, combined with the increased willingness of doting owners to spend on their companions’ care, has driven up the price of pet veterinary services. As a result, fewer and fewer vets have gone into farm animal practice. So the supply curve of farm vets has shifted leftward—fewer farm vets are offering their services at any given price.
In the end, farmers understand that it is all a matter of dollars and cents; they get fewer vets because they are unwilling or unable to pay more. As one farmer, who had recently lost an expensive cow due to the unavailability of a vet, stated, “The fact that there’s nothing you can do, you accept it as a business expense now. You didn’t used to. If you have livestock, sooner or later you’re going to have deadstock.”

Quick Review
The supply schedule shows how, all other things equal, the quantity supplied depends on the price. The supply curve illustrates this relationship.
Supply curves are normally upward sloping: at a higher price, all other things equal, producers are willing to supply more of a good or service.
A change in price, all other things equal, results in a movement along the supply curve and a change in the quantity supplied.
Increases or decreases in supply lead to shifts of the supply curve. An increase in supply is a rightward shift: the quantity supplied rises for any given price. A decrease in supply is a leftward shift: the quantity supplied falls for any given price.
The six main factors that can shift the supply curve are changes in (1) input prices, (2) prices of related goods or services, (3) technology, (4) weather, (5) expectations about future prices, and (6) number of producers.
The market supply curve is the horizontal sum of the individual supply curves of all producers in the market.
Check Your Understanding 3-2
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING 3-2
Question 3.2
Explain whether each of the following events represents (i) a shift of the supply curve or (ii) a movement along the supply curve.
More homeowners put their houses up for sale during a real estate boom that causes house prices to rise.
Many strawberry farmers open temporary roadside stands during harvest season, even though prices are usually low at that time.
Immediately after the school year begins, fast-food chains must raise wages, which represent the price of labour, to attract workers.
Due to favourable growing conditions, wheat farmers in the Prairie provinces experience bumper crops.
Since new technologies have made it possible to build larger cruise ships (which are cheaper to run per passenger), Caribbean cruise lines offer more cabins, at lower prices, than before.
The quantity of houses supplied rises as a result of an increase in prices. This is a movement along the supply curve.
The quantity of strawberries supplied is higher at any given price. This is a rightward shift of the supply curve.
The quantity of labour supplied is lower at any given wage. This is a leftward shift of the supply curve compared to the supply curve during school vacation. So, in order to attract workers, fast-food chains have to offer higher wages.
The quantity of wheat supplied is higher at any given price. This is a rightward shift of the supply curve.
The quantity of cabins supplied is higher at any given price. This is a rightward shift of the supply curve.