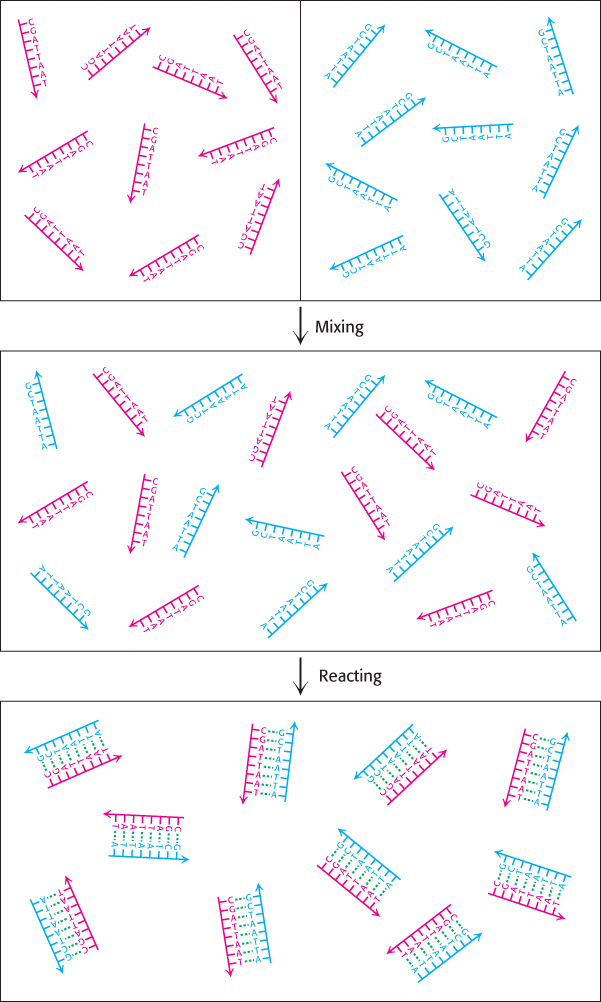
FIGURE 1.15 Double- helix formation and entropy. When solutions containing DNA strands with complementary sequences are mixed, the strands react to form double helices. This process results in a loss of entropy from the system, indicating that heat must be released to the surroundings to prevent a violation of the Second Law of Thermodynamics.
[Leave] [Close]