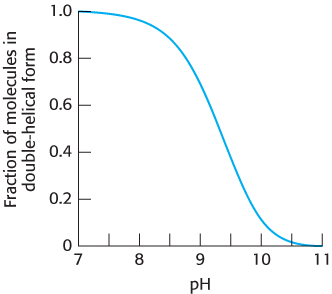
FIGURE 1.16 DNA denaturation by the addition of a base. The addition of a base to a solution of double- helical DNA initially at pH 7 causes the double helix to separate into single strands. The process is half complete at slightly above pH 9.
[Leave] [Close]