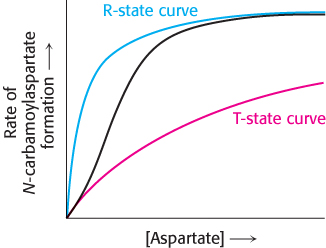
Basis for the sigmoidal curve. The generation of the sigmoidal curve by the property of cooperativity can be understood by imagining an allosteric enzyme as a mixture of two Michaelis–