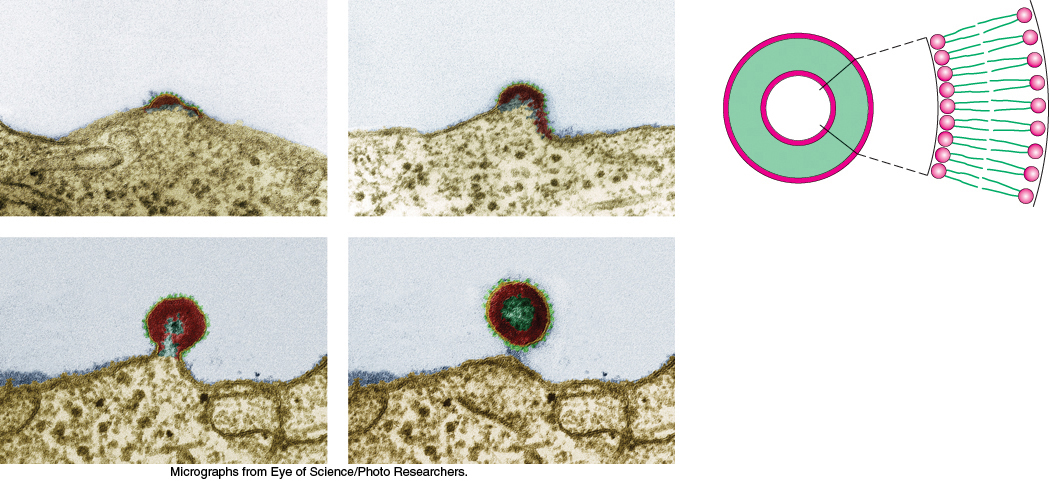
An HIV particle exits an infected cell by membrane budding. Cellular membranes are highly dynamic structures that spontaneously self-
[Micrographs from Eye of Science/Photo Researchers.]