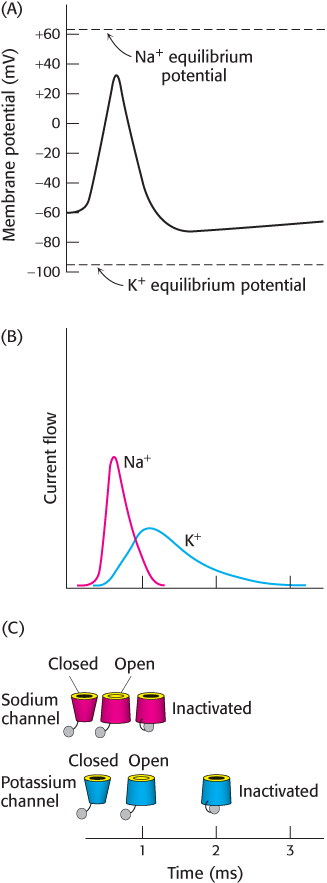
FIGURE 13.30 Action- potential mechanism. (A) On the initiation of an action potential, the membrane potential moves from the resting potential upward toward the Na+ equilibrium potential and then downward toward the K+ equilibrium potential. (B) The currents through the Na+ and K+ channels underlying the action potential. (C) The states of the Na+ and K+ channels during the action potential.
[Leave] [Close]