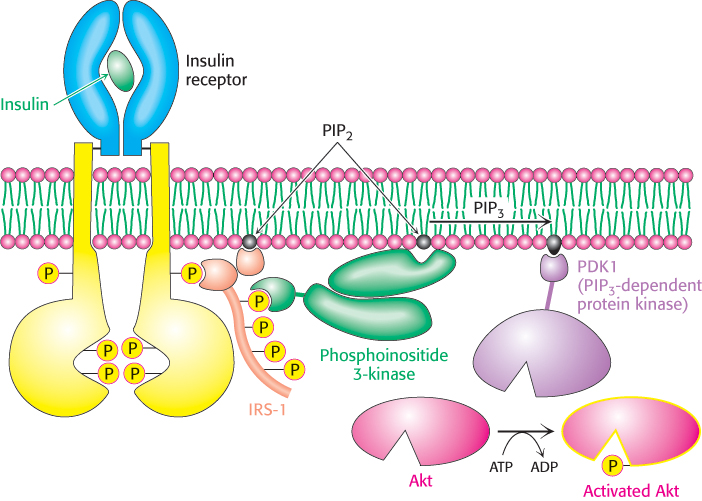
Insulin signaling. The binding of insulin results in the cross- n- S- 3- S- l-