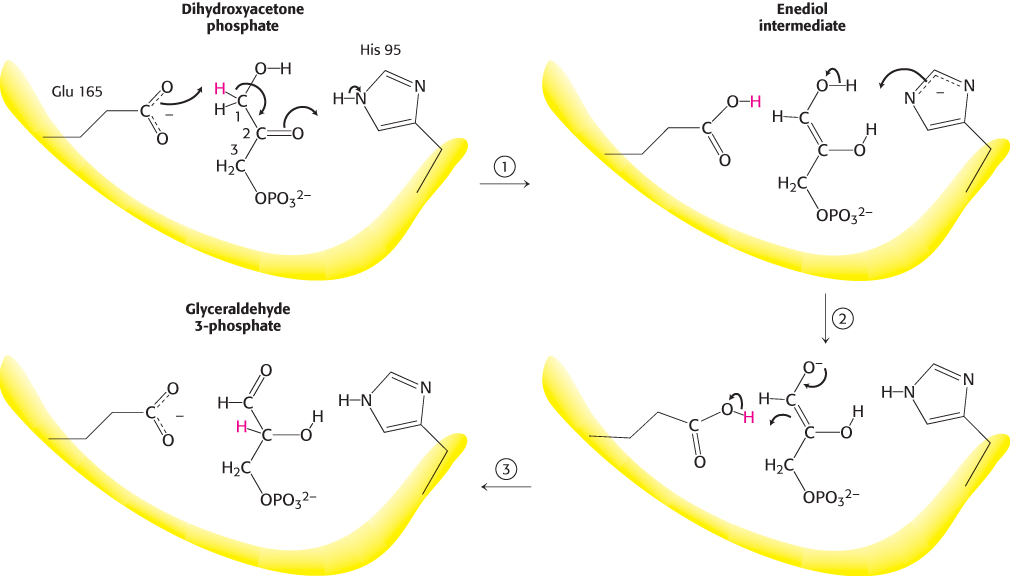
FIGURE 16.5 Catalytic mechanism of triose phosphate isomerase. (1) Glutamate 165 acts as a general base by abstracting a proton (H+) from carbon 1. Histidine 95, acting as a general acid, donates a proton to the oxygen atom bonded to carbon 2, forming the enediol intermediate. (2) Glutamic acid, now acting as a general acid, donates a proton to C- 2 while histidine removes a proton from the OH group of C- 1. (3) The product is formed, and glutamate and histidine are returned to their ionized and neutral forms, respectively.
[Leave] [Close]