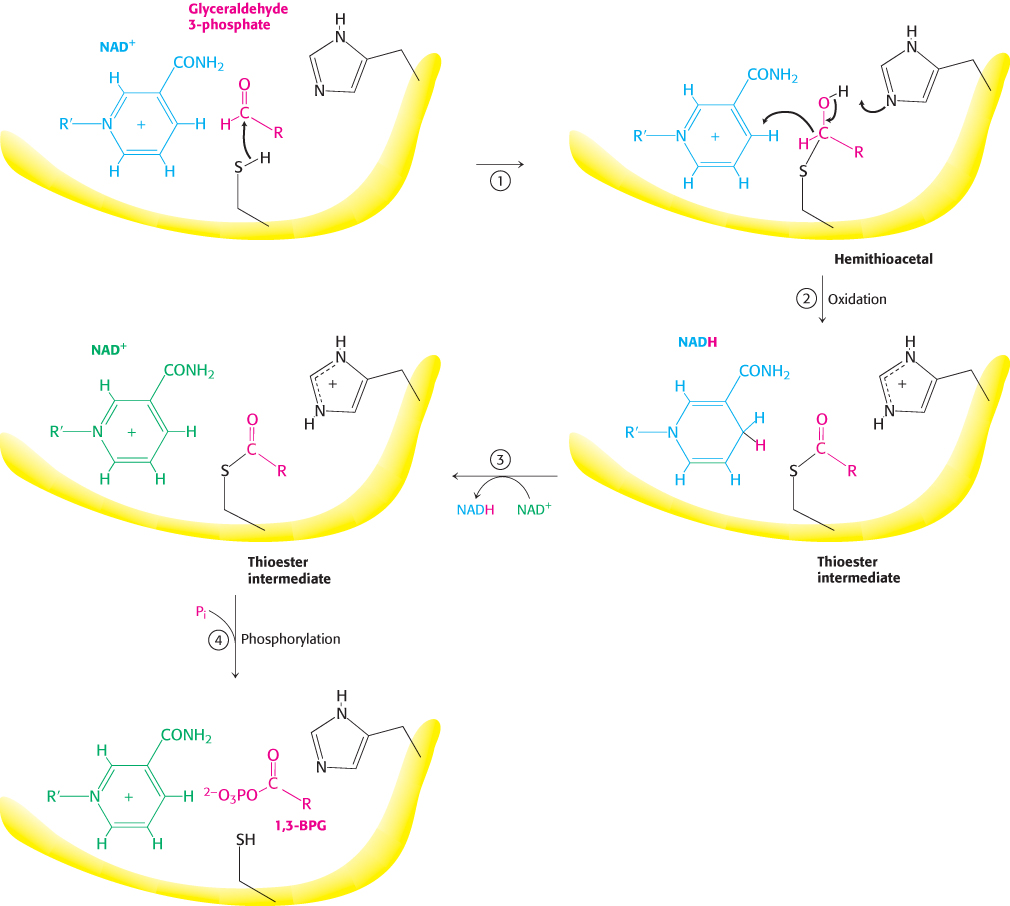
FIGURE 16.8 Catalytic mechanism of glyceraldehyde 3- phosphate dehydrogenase. The reaction proceeds through a thioester intermediate, which allows the oxidation of glyceraldehyde to be coupled to the phosphorylation of 3- phosphoglycerate. (1) Cysteine reacts with the aldehyde group of the substrate, forming a hemithioacetal. (2) An oxidation takes place with the transfer of a hydride ion to NAD+, forming a thioester. This reaction is facilitated by the transfer of a proton to histidine. (3) The reduced NADH is exchanged for an NAD+ molecule. (4) Orthophosphate attacks the thioester, forming the product 1,3- BPG.
[Leave] [Close]