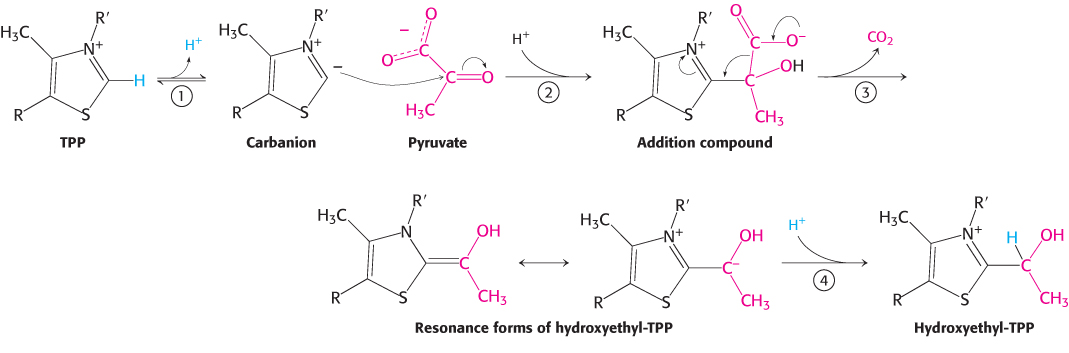
FIGURE 17.6 Mechanism of the E1 decarboxylation reaction. E1 is the pyruvate dehydrogenase component of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. A key feature of the prosthetic group, TPP, is that the carbon atom between the nitrogen and sulfur atoms in the thiazole ring is much more acidic than most =C— groups, with a pKa value near 10. (1) This carbon center ionizes to form a carbanion. (2) The carbanion readily adds to the carbonyl group of pyruvate. (3) This addition is followed by the decarboxylation of pyruvate. The positively charged ring of TPP acts as an electron sink that stabilizes the negative charge that is transferred to the ring as part of the decarboxylation. (4) Protonation yields hydroxyethyl- TPP.
[Leave] [Close]