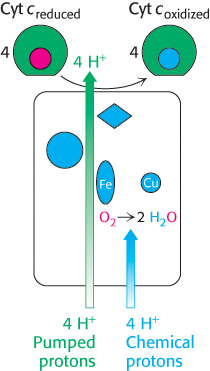
Proton transport by cytochrome c oxidase. Four protons are taken up from the matrix side to reduce one molecule of O2 to two molecules of H2O. These protons are called “chemical protons” because they participate in a clearly defined reaction with O2. Four additional “pumped” protons are transported out of the matrix and released on the cytoplasmic side in the course of the reaction. The pumped protons double the efficiency of free- n-