Oxidant | Reductant | n |
|
|---|---|---|---|
Succinate + CO2 | α-Ketoglutarate | 2 | −0.67 |
Acetate | Acetaldehyde | 2 | −0.60 |
Ferredoxin (oxidized) | Ferredoxin (reduced) | 1 | −0.43 |
2 H+ | H2 | 2 | −0.42 |
NAD+ | NADH + H+ | 2 | −0.32 |
NADP+ | NADPH + H+ | 2 | −0.32 |
Lipoate (oxidized) | Lipoate (reduced) | 2 | −0.29 |
Glutathione (oxidized) | Glutathione (reduced) | 2 | −0.23 |
FAD | FADH2 | 2 | −0.22 |
Acetaldehyde | Ethanol | 2 | −0.20 |
Pyruvate | Lactate | 2 | −0.19 |
2 H+ | H2 | 2 | −0.001 |
Fumarate | Succinate | 2 | +0.03 |
Cytochrome b (+3) | Cytochrome b (+2) | 1 | +0.07 |
Dehydroascorbate | Ascorbate | 2 | +0.08 |
Ubiquinone (oxidized) | Ubiquinone (reduced) | 2 | +0.10 |
Cytochrome c (+3) | Cytochrome c (+2) | 1 | +0.22 |
Fe (+3) | Fe (+2) | 1 | +0.77 |
½ O2 + 2 H+ | H2O | 2 | +0.82 |
Note: 1Standard oxidation − reduction potential at pH = 0. | |||
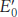 (V)
(V)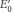 is the standard oxidatio
is the standard oxidatio