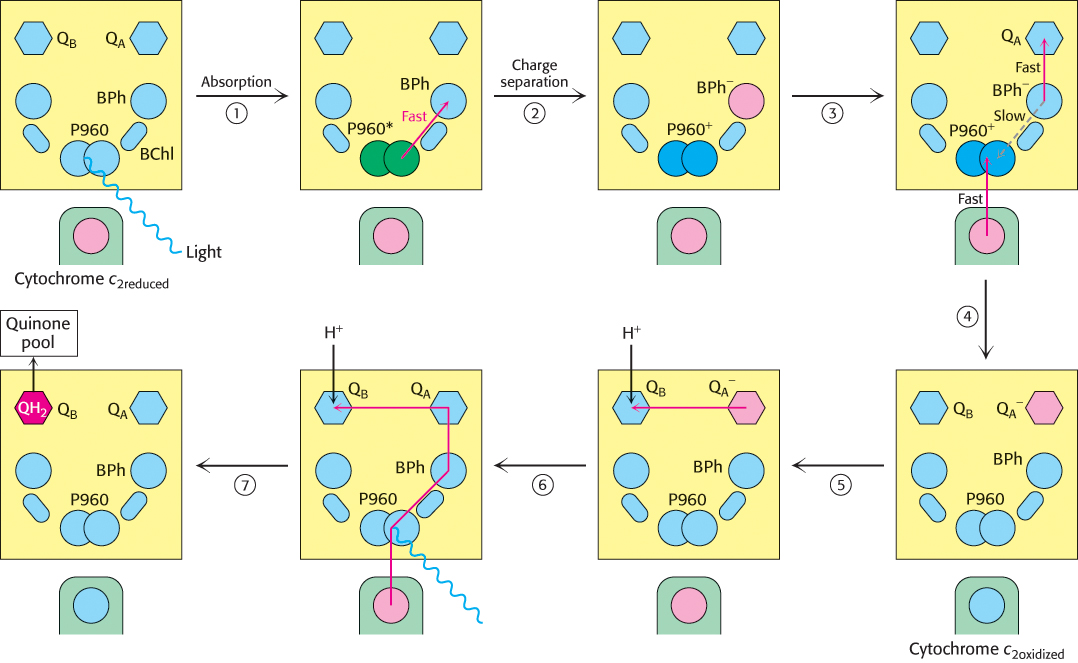
Electron chain in the photosynthetic bacterial reaction center. The absorption of light by the special pair (P960) results in the rapid transfer of an electron from this site to a bacteriopheophytin (BPh), creating a photoinduced charge separation (steps 1 and 2). (The asterisk on P960 stands for excited state.) The possible return of the electron from the pheophytin to the oxidized special pair is suppressed by the “hole” in the special pair being refilled with an electron from the cytochrome subunit and the electron from the pheophytin being transferred to a quinone (QA) that is farther away from the special pair (steps 3 and 4). QA passes the electron to QB. The reduction of a quinone (QB) on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane results in the uptake of two protons from the cytoplasm (steps 5 and 6). The reduced quinone can move into the quinone pool in the membrane (step 7).