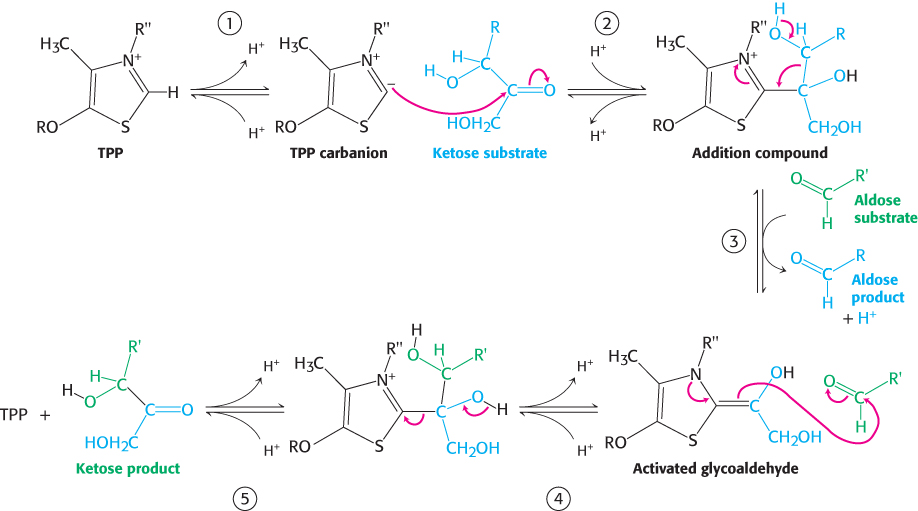
FIGURE 20.20 Transketolase mechanism. (1) Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) ionizes to form a carbanion. (2) The carbanion of TPP attacks the ketose substrate. (3) Cleavage of a carbon– carbon bond frees the aldose product and leaves a two- carbon fragment joined to TPP. (4) This activated glycoaldehyde intermediate attacks the aldose substrate to form a new carbon– carbon bond. (5) The ketose product is released, freeing the TPP for the next reaction cycle.
[Leave] [Close]