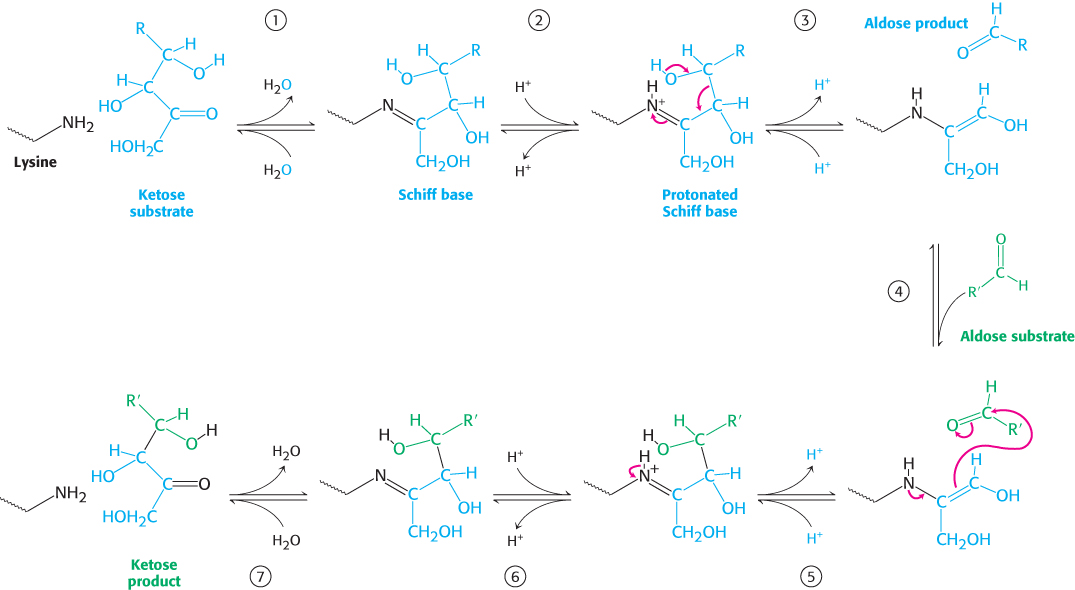
FIGURE 20.21 Transaldolase mechanism. (1) The reaction begins with the formation of a Schiff base between a lysine residue in transaldolase and the ketose substrate. (2) Protonation of the Schiff base occurs. (3) Deprotonation leads to the release of the aldose product, leaving a three- carbon fragment attached to the lysine residue. (4) This intermediate adds to the aldose substrate. (5) Protonation occurs, forming a new carbon– carbon bond. (6) Subsequent deprotonation and (7) hydrolysis of the Schiff base releases the ketose product from the lysine side chain, completing the reaction cycle.
[Leave] [Close]