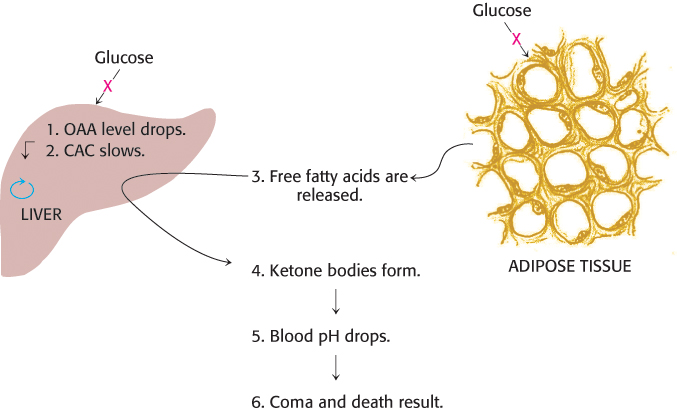
FIGURE 22.24 Diabetic ketosis results when insulin is absent. In the absence of insulin, fats are released from adipose tissue, and glucose cannot be absorbed by the liver or adipose tissue. The liver degrades the fatty acids by β oxidation but cannot process the acetyl CoA, because of a lack of glucose- derived oxaloacetate (OAA). Excess ketone bodies are formed and released into the blood.
[Leave] [Close]