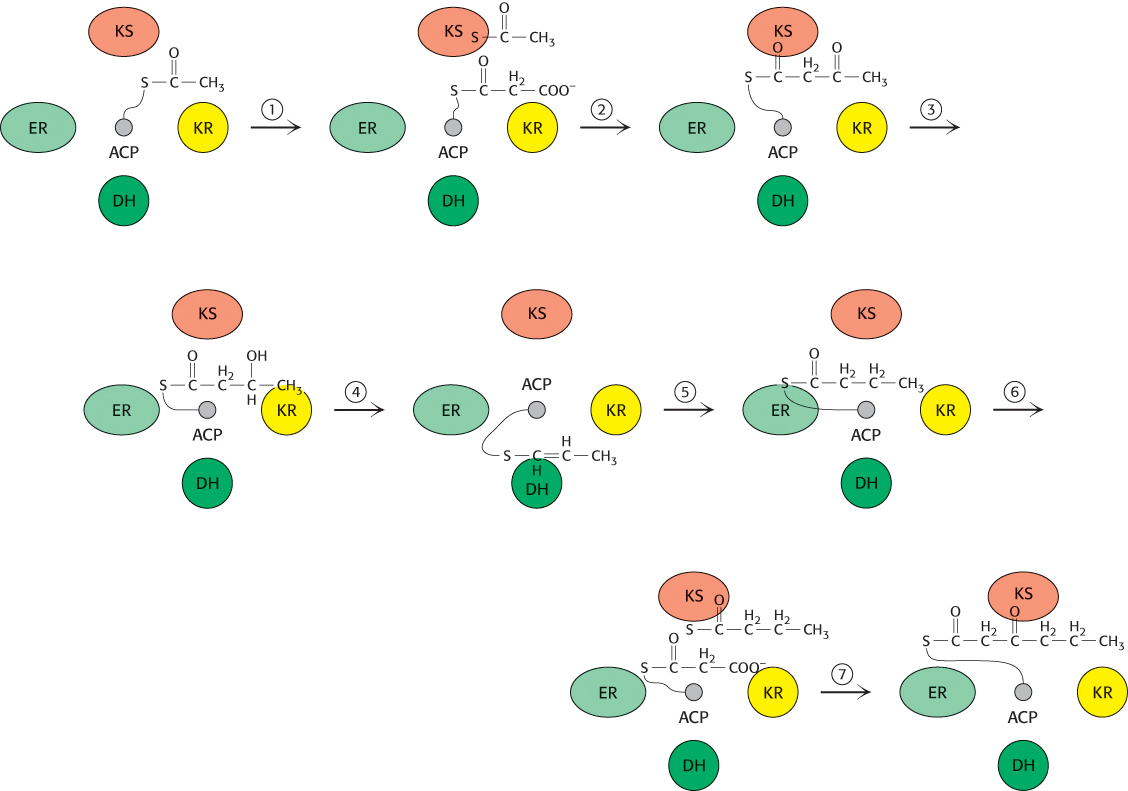
FIGURE 22.28 A catalytic cycle of mammalian fatty acid synthase. The cycle begins when MAT (not shown) attaches an acetyl unit to ACP. (1) ACP delivers the acetyl unit to KS, and MAT then attaches a malonyl unit to ACP. (2) ACP visits KS again, which condenses the acetyl and malonyl units to form the β-ketoacyl product, attached to the ACP. (3) ACP delivers the β-ketoacyl product to the KR enzyme, which reduces the keto group to an alcohol. (4) The β-hydroxyl product then visits the DH, which introduces a double bond with the loss of water. (5) The enoyl product is delivered to the ER enzyme, where the double bond is reduced. (6) ACP hands the reduced product to KS and is recharged with malonyl CoA by MAT. (7) KS condenses the two molecules on ACP, which is now ready to begin another cycle. See Figure 22.27 for abbreviations.
[Leave] [Close]