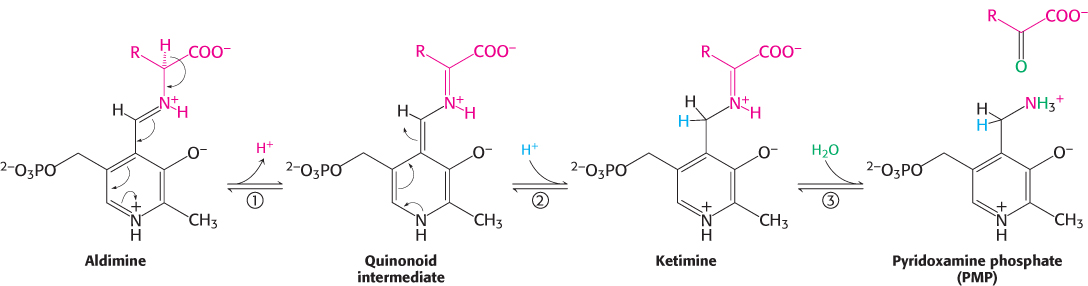
FIGURE 23.9 Transamination mechanism. (1) The external aldimine loses a proton to form a quinonoid intermediate. (2) Reprotonation of this intermediate at the aldehyde carbon atom yields a ketimine. (3) This intermediate is hydrolyzed to generate the α-ketoacid product and pyridoxamine phosphate.
[Leave] [Close]