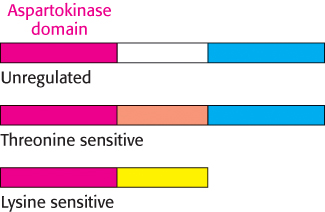
FIGURE 24.20 Domain structures of three aspartokinases. Each catalyzes the committed step in the biosynthesis of a different amino acid: (top) methionine, (middle) threonine, and (bottom) lysine. They have a catalytic domain in common (red) but differ in their regulatory domains (yellow and orange). The blue domain represents another enzyme (homoserine dehydrogenase) involved in aspartate metabolism. Thus, the top two aspartokinases are bifunctional enzymes.
[Leave] [Close]