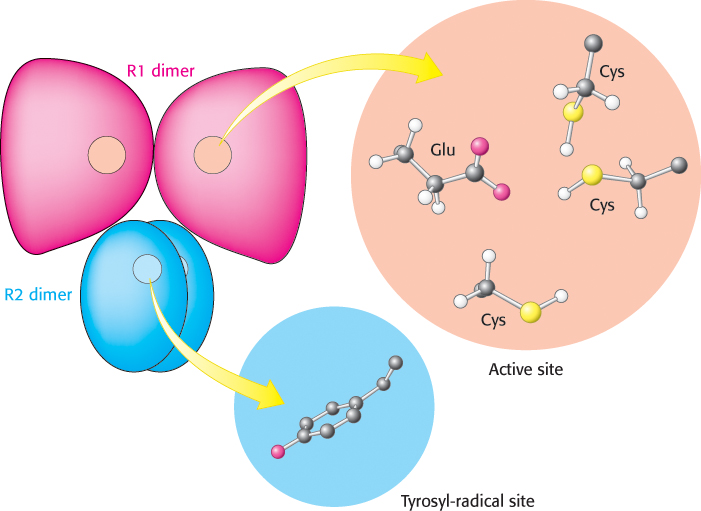
FIGURE 25.9 Ribonucleotide reductase. Ribonucleotide reductase reduces ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides in its active site, which contains three key cysteine residues and one glutamate residue. Each R2 subunit contains a tyrosyl radical that accepts an electron from one of the cysteine residues in the active site to initiate the reduction reaction. Two R1 subunits come together to form a dimer as do two R2 subunits.
[Leave] [Close]