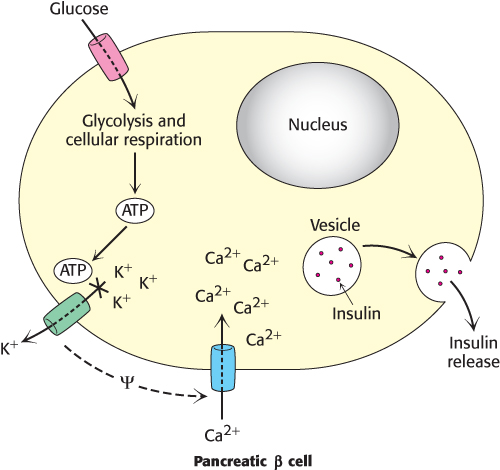
Insulin release is regulated by ATP. The metabolism of glucose by glycolysis and cellular respiration increases the concentration of ATP, which causes an ATP- n-