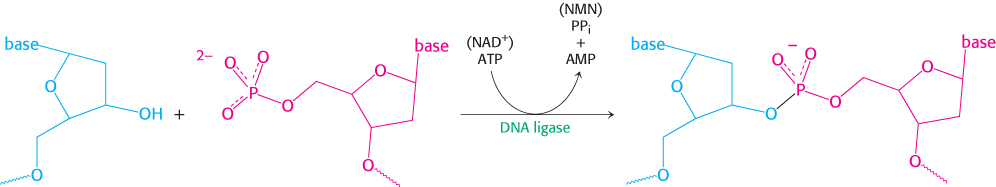
DNA ligase reaction. DNA ligase catalyzes the joining of one DNA strand with a free 3′-hydroxyl group to another with a free 5′-phosphoryl group. In eukaryotes and archaea, ATP is cleaved to AMP and PPi to drive this reaction. In bacteria, NAD+ is cleaved to AMP and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN).