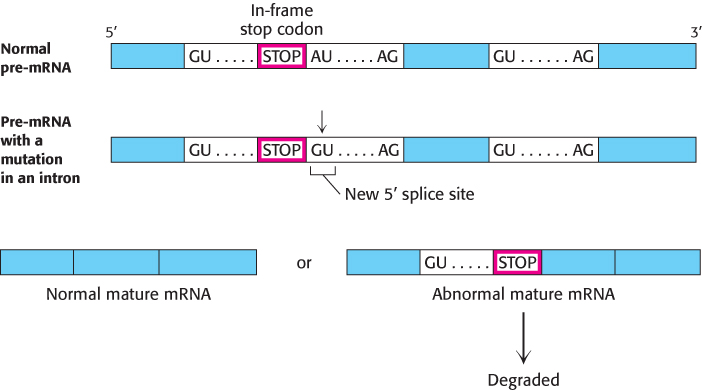
A splicing mutation that causes thalassemia. An A- o-