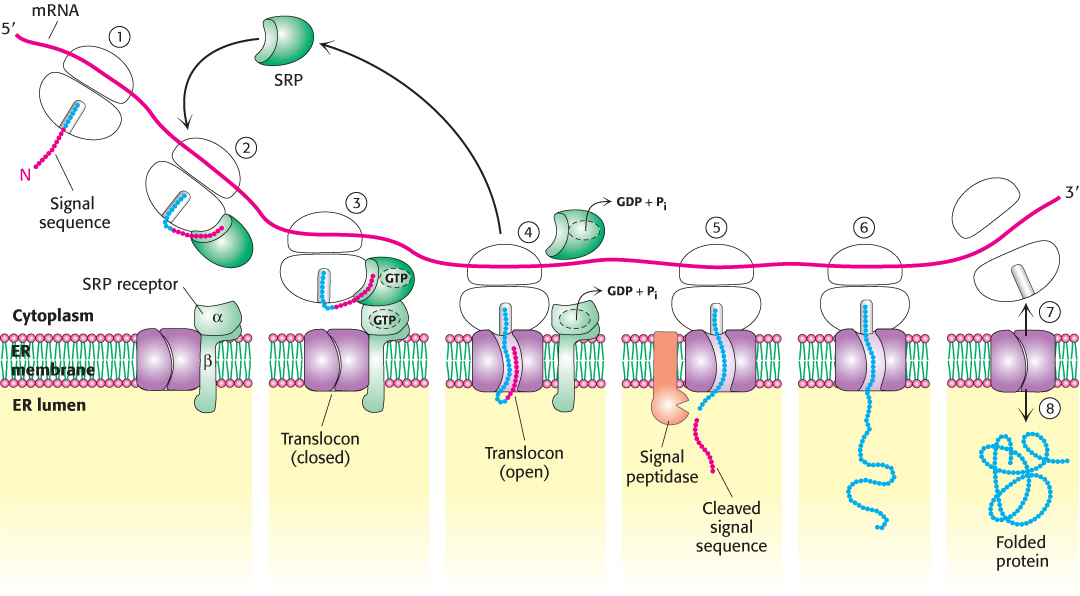
FIGURE 30.36 The SRP targeting cycle. (1) Protein synthesis begins on free ribosomes. (2) After the signal sequence has exited the ribosome, it is bound by the SRP, and protein synthesis halts. (3) The SRP– ribosome complex docks with the SRP receptor in the ER membrane. (4) The SRP and the SRP receptor simultaneously hydrolyze bound GTPs. Protein synthesis resumes and the SRP is free to bind another signal sequence. (5) The signal peptidase may remove the signal sequence as it enters the lumen of the ER. (6) Protein synthesis continues as the protein is synthesized directly into the ER. (7) On completion of protein synthesis, the ribosome is released. (8) The protein tunnel in the translocon closes.
[Information from H. Lodish et al., Molecular Cell Biology, 5th ed. (W. H. Freeman and Company, 2004), Fig. 16.6.]
[Leave] [Close]