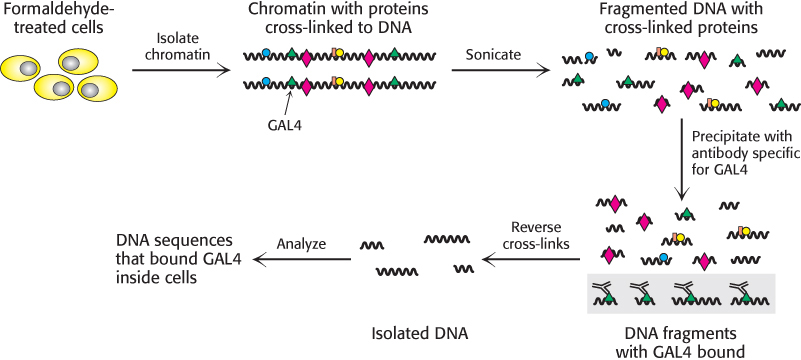
FIGURE 32.14 Chromatin immunoprecipitation. Cells or isolated nuclei are treated with formaldehyde to cross- link proteins to DNA. The cells are then lysed and the DNA is fragmented by sonication. DNA fragments bound to a particular protein are isolated through the use of an antibody specific for that protein. The cross- links are then reversed and the DNA fragments are characterized.
[Leave] [Close]