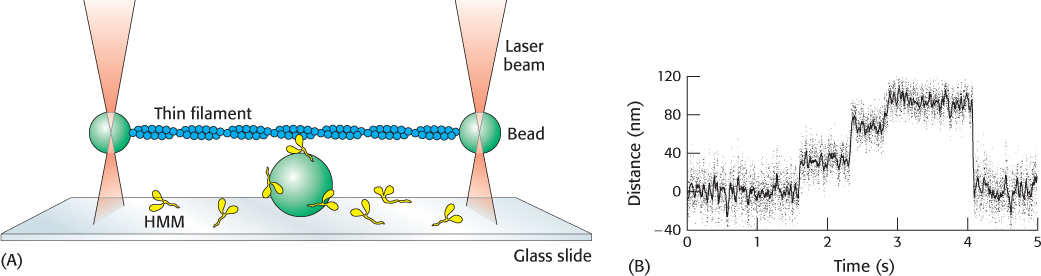
FIGURE 35.14 Watching a single motor protein in action. (A) An actin filament (blue) is placed above a heavy meromyosin (HMM) fragment (yellow) that projects from a bead on a glass slide. A bead attached to each end of the actin filament is held in an optical trap produced by a focused, intense infrared laser beam (orange). The position of these beads can be measured with nanometer precision. (B) Recording of the displacement of an actin filament due to a myosin derivative attached to a bead, influenced by the addition of ATP. Note the fairly uniform step sizes that are observed.
[(A) Information from J. T. Finer, R. M. Simmons, and J. A. Spudich, Nature 368:113– 119, 1994. (B) Data from R. S. Rock, M. Rief, A. D. Metra, and J. A. Spudich, Methods 22:378– 381, 2000.]
[Leave] [Close]