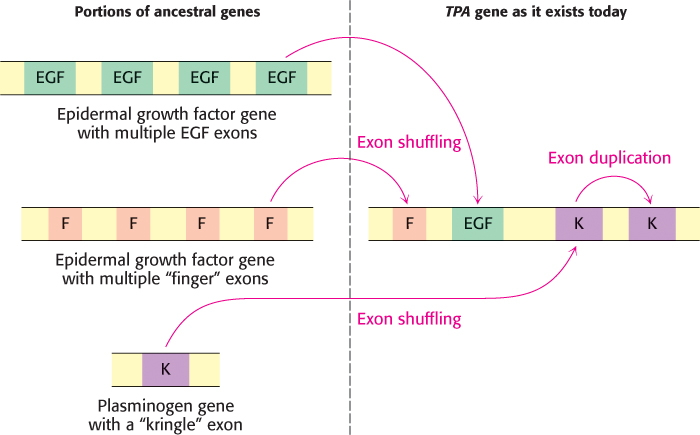
FIGURE 4.41 The tissue plasminogen activator (TPA) gene was generated by exon shuffling. The gene for TPA encodes an enzyme that functions in hemostasis (Section 10.4). This gene consists of 4 exons, one (F) derived from the fibronectin gene which encodes an extracellular matrix protein, one from the epidermal growth factor gene (EGF), and two from the plasminogen gene (K, Section 10.4), the substrate of the TPA protein. The K domain appears to have arrived by exon shuffling and then been duplicated to generate the TPA gene that exists today.
[Leave] [Close]