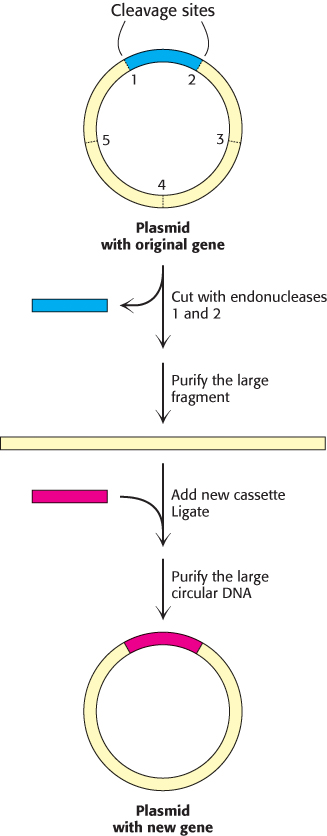
FIGURE 5.23 Cassette mutagenesis. DNA is cleaved at a pair of unique restriction sites by two different restriction endonucleases. A synthetic oligonucleotide with ends that are complementary to these sites (the cassette) is then ligated to the cleaved DNA. The method is highly versatile because the inserted DNA can have any desired sequence.
[Leave] [Close]