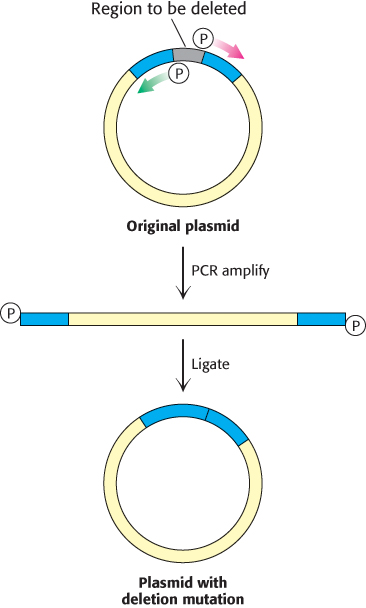
FIGURE 5.24 Deletion mutagenesis by inverse PCR. A deletion can be introduced into a plasmid with primers that flank this region but are oriented away from the segment to be removed. PCR amplification yields a linear product that contains the entire plasmid minus the unwanted sequence. If the primers contained a 5’ phosphate group, this product can be recircularized using DNA ligase, generating a plasmid with the desired mutation.
[Leave] [Close]