PROBLEMS
PROBLEMS
Question 8.1
Raisons d’être. What are the two properties of enzymes that make them especially useful catalysts?
Question 8.2
Partners. What does an apoenzyme require to become a holoenzyme?
Question 8.3
Different partners. What are the two main types of cofactors?
Question 8.4
One a day. Why are vitamins necessary for good health?
Question 8.5
A function of state. What is the fundamental mechanism by which enzymes enhance the rate of chemical reactions?
Question 8.6
Nooks and crannies. What is the structural basis for enzyme specificity?
Question 8.7
Give with one hand, take with the other. Why does the activation energy of a reaction not appear in the final ΔG of the reaction?
Question 8.8
The more things change, the more they stay the same. Suppose that, in the absence of enzyme, the forward rate constant (kF) for the conversion of S into P is 10−4 s−1 and the reverse rate constant (kR) for the conversion of P into S is 10−6 s−1.
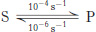
What is the equilibrium for the reaction? What is the ΔG°′?
Suppose an enzyme enhances the rate of the reaction 100 fold. What are the rate constants for the enzyme-
catalyzed reaction? The equilibrium constant? The ΔG°′?
Question 8.9
Mountain climbing. Proteins are thermodynamically unstable. The ΔG of the hydrolysis of proteins is quite negative, yet proteins can be quite stable. Explain this apparent paradox. What does it tell you about protein synthesis?
Question 8.10
Protection. Suggest why the enzyme lysozyme, which degrades cell walls of some bacteria, is present in tears.
Question 8.11
Mutual attraction. What is meant by the term binding energy?
Question 8.12
Catalytically binding. What is the role of binding energy in enzyme catalysis?
Question 8.13
Sticky situation. What would be the result of an enzyme having a greater binding energy for the substrate than for the transition state?
Question 8.14
Stability matters. Transition-
Question 8.15
Match’em. Match the  values with the appropriate ΔG°′ values.
values with the appropriate ΔG°′ values.
|
|
|
ΔG°′(kJ mol−1) |
|
(a) |
1 |
28.53 |
|
(b) |
10−5 |
−11.42 |
|
(c) |
104 |
5.69 |
|
(d) |
102 |
0 |
|
(e) |
10−1 |
−22.84 |
Question 8.16
Free energy! Assume that you have a solution of 0.1 M glucose 6-
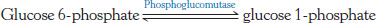
The ΔG°′ for the reaction is +7.5 kJ mol−1 (+1.8 kcal mol−1).
Does the reaction proceed as written? If so, what are the final concentrations of glucose 6-
phosphate and glucose 1- phosphate? Under what cellular conditions could you produce glucose 1-
phosphate at a high rate?
Question 8.17
Free energy, too! Consider the following reaction:
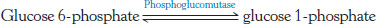
After reactant and product were mixed and allowed to reach equilibrium at 25°C, the concentration of each compound was measured:
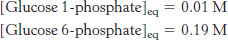
Calculate Keq and ΔG°′.
Question 8.18
Keeping busy. Many isolated enzymes, if incubated at 37°C, will be denatured. However, if the enzymes are incubated at 37°C in the presence of substrate, the enzymes are catalytically active. Explain this apparent paradox.
Question 8.19
Active yet responsive. What is the biochemical advantage of having a KM approximately equal to the substrate concentration normally available to an enzyme?
Question 8.20
Affinity or not affinity? That is the question. The affinity between a protein and a molecule that binds to the protein is frequently expressed in terms of a dissociation constant Kd.
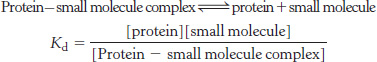
Does KM measure the affinity of the enzyme complex? Under what circumstances might KM approximately equal Kd?
247
Question 8.21
Angry biochemists. Many biochemists go bananas, and justifiably, when they see a Michaelis–
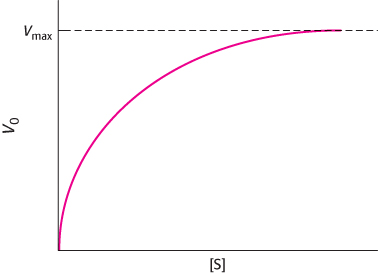
Question 8.22
Hydrolytic driving force. The hydrolysis of pyrophosphate to orthophosphate is important in driving forward biosynthetic reactions such as the synthesis of DNA. This hydrolytic reaction is catalyzed in E. coli by a pyrophosphatase that has a mass of 120 kDa and consists of six identical subunits. For this enzyme, a unit of activity is defined as the amount of enzyme that hydrolyzes 10 μmol of pyrophosphate in 15 minutes at 37°C under standard assay conditions. The purified enzyme has a Vmax of 2800 units per milligram of enzyme.
How many moles of substrate is hydrolyzed per second per milligram of enzyme when the substrate concentration is much greater than KM?
How many moles of active sites are there in 1 mg of enzyme? Assume that each subunit has one active site.
What is the turnover number of the enzyme? Compare this value with others mentioned in this chapter.
Question 8.23
Destroying the Trojan horse. Penicillin is hydrolyzed and thereby rendered inactive by penicillinase (also known as β-lactamase), an enzyme present in some penicillin-
|
[Penicillin] μM |
Amount hydrolyzed (nmol) |
|---|---|
|
1 |
0.11 |
|
3 |
0.25 |
|
5 |
0.34 |
|
10 |
0.45 |
|
30 |
0.58 |
|
50 |
0.61 |
Plot V0 versus [S] and 1/V0 versus 1/[S] for these data. Does penicillinase appear to obey Michaelis–
Menten kinetics? If so, what is the value of KM? What is the value of Vmax?
What is the turnover number of penicillinase under these experimental conditions? Assume one active site per enzyme molecule.
Question 8.24
Counterpoint. Penicillinase (β-lactamase) hydrolyzes penicillin. Compare penicillinase with glycopeptide transpeptidase.
Question 8.25
A different mode. The kinetics of an enzyme is measured as a function of substrate concentration in the presence and absence of 100 μM inhibitor.
What are the values of Vmax and KM in the presence of this inhibitor?
What type of inhibition is it?
What is the dissociation constant of this inhibitor?
Velocity (μmol minute−1)
[S] (μM)
No inhibitor
Inhibitor
3
10.4
2.1
5
14.5
2.9
10
22.5
4.5
30
33.8
6.8
90
40.5
8.1
If [S] = 30 μM, what fraction of the enzyme molecules have a bound substrate in the presence and in the absence of 100 μM inhibitor?
Question 8.26
A fresh view. The plot of 1/V0 versus 1/[S] is sometimes called a Lineweaver–
Rearrange the Michaelis–
Menten equation to give V0 as a function of V0/[S]. What is the significance of the slope, the y-intercept, and the x-intercept in a plot of V0 versus V0/[S]?
Sketch a plot of V0 versus V0/[S] in the absence of an inhibitor, in the presence of a competitive inhibitor, and in the presence of a noncompetitive inhibitor.
Question 8.27
Defining attributes. What is the defining characteristic for an enzyme catalyzing a sequential reaction? A double-
Question 8.28
Competing substrates. Suppose that two substrates, A and B, compete for an enzyme. Derive an expression relating the ratio of the rates of utilization of A and B, VA/VB, to the concentrations of these substrates and their values of kcat and KM. (Hint: Express VA as a function of kcat/KM for substrate A, and do the same for VB.) Is specificity determined by KM alone?
248
Question 8.29
A tenacious mutant. Suppose that a mutant enzyme binds a substrate 100 times as tightly as does the native enzyme. What is the effect of this mutation on catalytic rate if the binding of the transition state is unaffected?
Question 8.30
More Michaelis–
Question 8.31
Controlled paralysis. Succinylcholine is a fast-
As a safety measure, serum cholinesterase is measured before the examination takes place. Explain why this measurement is good idea.
What would happen to the patient if the serum cholinesterase activity were only 10 units of activity per liter rather than the normal activity of about 80 units?
Some patients have a mutant form of the serum cholinesterase that displays a KM of 10 mM, rather than the normal 1.4 mM. What will be the effect of this mutation on the patient?
Data Interpretation Problems
Question 8.32
A natural attraction, but more complicated. You have isolated two versions of the same enzyme, a wild type and a mutant differing from the wild type at a single amino acid. Working carefully but expeditiously, you then establish the following kinetic characteristics of the enzymes.
|
|
Maximum velocity |
KM |
|---|---|---|
|
Wild type |
100 μmol/min |
10 mM |
|
Mutant |
1 μmol/min |
0.1 mM |
With the assumption that the reaction occurs in two steps in which k−1 is much larger than k2, which enzyme has the higher affinity for substrate?
What is the initial velocity of the reaction catalyzed by the wild-
type enzyme when the substrate concentration is 10 mM? Which enzyme alters the equilibrium more in the direction of product?
Question 8.33
KM matters. The amino acid asparagine is required by cancer cells to proliferate. Treating patients with the enzyme asparaginase is sometimes used as a chemotherapy treatment. Asparaginase hydrolyzes asparagine to aspartate and ammonia. The adjoining illustration shows the Michaelis–
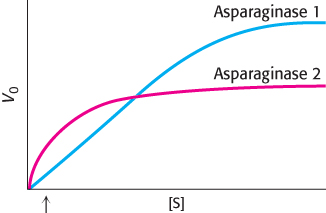
Question 8.34
Enzyme specificity. Catalysis of the cleavage of peptide bonds in small peptides by a proteolytic enzyme is described in the following table.
|
Substrate |
KM (mM) |
kcat(s−1) |
|---|---|---|
|
EMTA↓G |
4.0 |
24 |
|
EMTA↓A |
1.5 |
30 |
|
EMTA↓F |
0.5 |
18 |
The arrow indicates the peptide bond cleaved in each case.
If a mixture of these peptides were presented to the enzyme with the concentration of each peptide being the same, which peptide would be digested most rapidly? Most slowly? Briefly explain your reasoning, if any.
The experiment is performed again on another peptide with the following results.
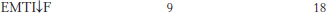
On the basis of these data, suggest the features of the amino acid sequence that dictate the specificity of the enzyme.
Question 8.35
Varying the enzyme. For a one-
249
Question 8.36
Mental experiment. Picture in your mind the velocity vs. substrate concentration curve for a typical Michaelis-
|
Experimental condition |
Vmax |
KM |
|---|---|---|
|
a. Twice as much enzyme is used. |
|
|
|
b. Half as much enzyme is used |
|
|
|
c. A competitive inhibitor is present. |
|
|
|
d. An uncompetitive inhibitor is present. |
|
|
|
e. A pure non- |
|
|
Question 8.37
Too much of a good thing. A simple Michaelis–
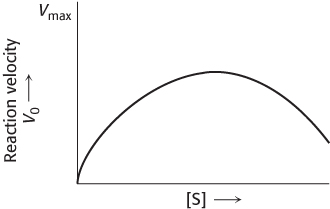
Draw a double-
reciprocal plot that corresponds to the velocity- versus- substrate curve. Suggest a plausible explanation for these kinetic results.
Question 8.38
Rate-
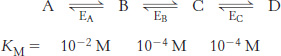
Question 8.39
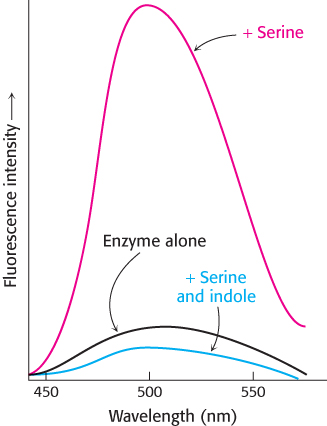
Colored luminosity Tryptophan synthetase, a bacterial enzyme that contains a pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) prosthetic group, catalyzes the synthesis of l-tryptophan from l-serine and an indole derivative. The addition of l-serine to the enzyme produces a marked increase in the fluorescence of the PLP group, as the adjoining graph shows. The subsequent addition of indole, the second substrate, reduces this fluorescence to a level even lower than that produced by the enzyme alone. How do these changes in fluorescence support the notion that the enzyme interacts directly with its substrates?
Chapter Integration Problems
Question 8.40
Titration experiment. The effect of pH on the activity of an enzyme was examined. At its active site, the enzyme has an ionizable group that must be negatively charged for substrate binding and catalysis to take place. The ionizable group has a pKa of 6.0. The substrate is positively charged throughout the pH range of the experiment.
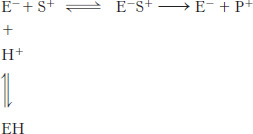
Draw the V0-versus-
pH curve when the substrate concentration is much greater than the enzyme KM. Draw the V0-versus-
pH curve when the substrate concentration is much less than the enzyme KM. At which pH will the velocity equal one-
half of the maximal velocity attainable under these conditions?
Question 8.41
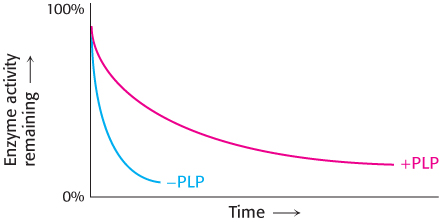
A question of stability. Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) is a coenzyme for the enzyme ornithine aminotransferase. The enzyme was purified from cells grown in PLP-
250
Why does the amount of active enzyme decrease with the time of incubation?
Why does the amount of enzyme from the PLP-
deficient cells decline more rapidly?
Question 8.42
Not just for enzymes. Kinetics is useful for studying reactions of all types, not just those catalyzed by enzymes. In Chapters 4 and 5, we learned that DNA could be reversibly melted. When melted double-