ANSWERS TO PROBLEMS
CHAPTER
102
A1
Chapter 1
1. The hydrogen-
2. Interchange the positions of the single and double bonds in the six-
3. (a) Ionic interactions; (b) van der Waals interactions.
4. Processes a and b.
5. ΔSsystem = −661 J mol−1 K−1(−158 kcal mol−1K−1)
ΔSsurroundings = +842 J mol−1K−1(+201 cal mol−1K−1)
6. (a) 1.0; (b) 13.0; (c) 1.3; (d) 12.7
7. 2.88
8. 1.96
9. 55.5 M
10. 11.83
11. 447; 0.00050
12. 0.00066 M
13. 6.0
14. 5.53
15. 6.48
16. 7.8
17. 100
18. (a) 1.6; (b) 0.51; (c) 0.16.
19.
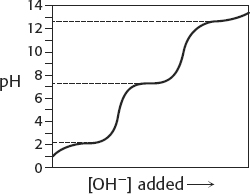
20. 0.1 M sodium acetate solution: 6.34; 6.03; 5.70; 4.75. 0.01 M sodium acetate solution: 5.90; 4.75; 3.38; 1.40.
21. 90 mM acetic acid; 160 mM sodium acetate, 0.18 moles acetic acid; 0.32 moles sodium acetate; 10.81 g acetic acid; 26.25 g sodium acetate.
22. 0.50 moles of acetic acid; 0.32 moles of NaOH; 30.03 g of acetic acid; 12.80 g of NaOH.
23. 250 mM; yes; no, it will also contain 90 mM NaCl.
24. 8.63 g Na2HPO4; 4.71 g NaH2PO4
25. 7.0; this buffer will not be very useful, because the pH value is far from the pKa value.
26. +1.45 kJ mol−1 (+0.35 kcal mol−1); +57.9 kJ mol−1 (+13.8 kcal mol−1)
27. There will be approximately 15 million differences.
28. (20!)/(10!*10!) = 184,756
29. 7.9%