Chapter 36
Chapter 36
1. (a) Before; (b) after; (c) after; (d) after; (e) before; (f ) after.
2. (a) Yes; (b) yes; (c) no (MW > 600).
3. If computer programs could estimate log(P) values on the basis of chemical structure, then the required laboratory time for drug development could be shortened. The determination of the relative solubilities of pharmaceutical candidates by allowing each compound to equilibrate between water and an organic phase would no longer be necessary.
4. Perhaps N-acetylcysteine would conjugate to some of the N-acetyl-
5. In Phase I clinical trials, approximately 10 to 100 usually healthy volunteers are typically enrolled in a study designed to assess safety. In contrast, a larger number of subjects are enrolled in a typical Phase II trial. Moreover, these persons may benefit from the drug administered. In a Phase II trial, efficacy, dosage, and safety can be assessed.
6. The binding of other drugs to albumin could cause extra coumadin to be released. (Albumin is a general carrier for hydrophobic molecules.)
7. A drug that inhibits a P450 enzyme may dramatically affect the disposition of another drug that is metabolized by that same enzyme. If this inhibited metabolism is not accounted for when dosing, the second drug may reach very high, and sometimes toxic, levels in the blood.
8. Unlike competitive inhibition, noncompetitive inhibition cannot be overcome with additional substrate. Hence, a drug that acts by a noncompetitive mechanism will be unaffected by changing levels of the physiological substrate.
9. An inhibitor of MDR could prevent the efflux of a chemotherapeutic drug from tumor cells. Hence, this type of an inhibitor could be useful in averting resistance to cancer chemotherapy.
10. Agents that inhibit one or more enzymes of the glycolytic pathway could act to deprive trypanosomes of energy and thus be useful for treating sleeping sickness. A difficulty is that glycolysis in the host cells also would be inhibited.
11. Imatinib is an inhibitor of the Bcr-
A48
12. Sildenafil increases cGMP levels by inhibiting the phosphodiesterase-
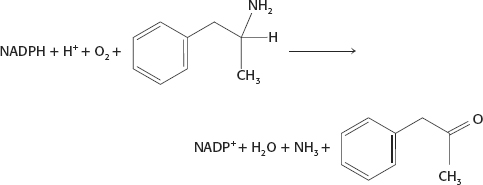
13. A reasonable mechanism would be an oxidative deamination following an overall mechanism similar to that in Figure 36.10, with release of ammonia.
14. KI ≈ 0.3 nM. IC50 ≈ 2.0 nM. Yes, compound A should be effective when taken orally because 400 nM is much greater than the estimated values of KI and IC50.