Chapter 6
Chapter 6
1. There are 26 identities and two gaps for a score of 210. The two sequences are approximately 26% identical. This level of homology is likely to be statistically significant.
2. They are likely related by divergent evolution, because three-
3. (1) Identity score = −25; Blosum score = 14; (2) identity score = 15; Blosum score = 3.
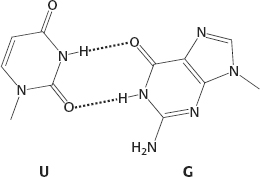
4. U. One possible structure:
5. There are 440, or 1.2 × 1024, different molecules. Each molecule has a mass of 2.2 × 10−20, because 1 mol of polymer has a mass of 330 g mol−1 × 40, and there are 6.02 × 1023 molecules per mole. Therefore, 26.4 kg of RNA would be required.
6. Because three-
7. Alignment score of sequences (1) and (2) is 6 × 10 = 60. Many answers are possible, depending on the randomly reordered sequence. A possible result is
|
Shuffled sequence: |
(2) TKADKAGEYL |
|
Alignment: |
(1) ASNFLDKAGK (2) TKADKAGEYL |
Alignment score is 4 × 10 = 40.
8. (a) Almost certainly diverged from a common ancestor. (b) Almost certainly diverged from a common ancestor. (c) May have diverged from a common ancestor, but the sequence alignment may not provide supporting evidence. (d) May have diverged from a common ancestor, but the sequence alignment is unlikely to provide supporting evidence.
9. Replacement of cysteine, glycine, and proline never yields a positive score. Each of these residues exhibits features unlike those of its other 19 counterparts: cysteine is the only amino acid capable of forming disulfide bonds, glycine is the only amino acid without a side-
10. Protein A is clearly homologous to protein B, given 65% sequence identity, and so A and B are expected to have quite similar three-
11. The likely secondary structure is
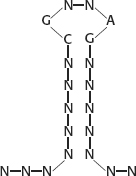
12. To detect pairs of residues with correlated mutations, there must be variability in these sequences. If the alignment is over-
13. After RNA molecules have been selected and reverse transcribed, PCR is performed to introduce additional mutations into these strands. The use of this error-
14. The initial pool of RNA molecules used in a molecular-
A8
Mutagenesis of the initial selected RNA molecules allows for the iterative improvement of these sequences for the desired property.
15. 107 or 108 identities (depending on which annotated human sequence is chosen).