PROBLEMS
PROBLEMS
Question 27.1
Weight control. As disturbing as the obesity epidemic is, an equally intriguing, almost amazing observation is that many people are able to maintain an approximately constant weight throughout adult life. A few simple calculations of a simplified situation illustrates how remarkable this feat is. Consider a 120-
Question 27.2
Spare tire. Suppose that our test subject from problem 1 gained 55 pounds between the ages of 25 and 65 (a sadly common occurrence), and that her weight at 65 years of age is 175 pounds. Calculate how many excess calories she consumed per day to gain the 55 pounds over 40 years. Assume that our test subject is 5 feet 6 inches tall. What is her BMI? Would she be considered obese at 175 lbs?
Question 27.3
Depot fat. Adipose tissue was once only considered a storage site for fat. Why is this view no longer considered correct?
Question 27.4
Balancing act. What is meant by caloric homeostasis?
Question 27.5
Dynamic duo. What are the key hormones responsible for maintaining caloric homeostasis?
Question 27.6
Dual roles. What two biochemical roles does CCK play? GLP-
Question 27.7
Failure to communicate. Leptin inhibits eating and is secreted in amounts in direct proportion to body fat. Moreover, obese people have normal amounts of leptin and leptin receptor. Why, then, do people become obese?
Question 27.8
Many signals. Match the characteristic (a–
|
|
Question 27.9
A key chemical. What are the sources of glucose 6-
Question 27.10
Neither option is good. Differentiate between type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Question 27.11
Fighting diabetes. Leptin is considered an “anti-
Question 27.12
Metabolic energy and power. The rate of energy expenditure of a typical 70-
Express this rate in kilojoules per second and in kilocalories per second.
How many electrons flow through the mitochondrial electron-
transport chain per second under these conditions? Estimate the corresponding rate of ATP production.
825
The total ATP content of the body is about 50 g. Estimate how often an ATP molecule turns over in a person at rest.
Question 27.13
Respiratory quotient (RQ). This classic metabolic index is defined as the volume of CO2 released divided by the volume of O2 consumed.
Calculate the RQ values for the complete oxidation of glucose and of tripalmitoylglycerol.
What do RQ measurements reveal about the contributions of different energy sources during intense exercise? (Assume that protein degradation is negligible.)
Question 27.14
Camel’s hump. Compare the H2O yield from the complete oxidation of 1 g of glucose with that of 1 g of tripalmitoylglycerol. Relate these values to the evolutionary selection of the contents of a camel’s hump.
Question 27.15
Hungry–
Question 27.16
Of course, too much is bad for you. What are the primary means of processing ethanol?
Question 27.17
Started out with burgundy, but soon hit the harder stuff. Describe the three stages of ethanol consumption that lead to liver damage and possibly death.
Question 27.18
The wages of sin. How long does a person have to jog to offset the calories obtained from eating 10 macadamia nuts (75 kJ, or 18 kcal, per nut)? (Assume an incremental power consumption of 400 W.)
Question 27.19
Sweet hazard. Ingesting large amounts of glucose before a marathon might seem to be a good way of increasing the fuel stores. However, experienced runners do not ingest glucose before a race. What is the biochemical reason for their avoidance of this potential fuel? (Hint: Consider the effect of glucose ingestion on the level of insulin.)
Question 27.20
Lipodystrophy. Lipodystrophy is a condition in which an individual lacks adipose tissue. The muscles and liver from such individuals are insulin resistant, and both tissues accumulate large amounts of triacylglycerols (hyperlipidemia). The administration of leptin partly ameliorates this condition. What does it indicate about the relation of adipose tissue to insulin action?
Question 27.21
Therapeutic target. What would be the effect of a mutation in the gene for PTP1B (protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B) that inactivated the enzyme in a person who has type 2 diabetes?
Question 27.22
An effect of diabetes. Insulin-
Question 27.23
Sharing the wealth. The hormone glucagon signifies the starved state, yet it inhibits glycolysis in the liver. How does this inhibition of an energy-
Question 27.24
Compartmentation. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm, whereas fatty acid degradation takes place in mitochondria. What metabolic pathways depend on the interplay of reactions that take place in both compartments?
Question 27.25
Kwashiorkor. The most common form of malnutrition in children in the world, kwashiorkor, is caused by a diet having ample calories but little protein. The high levels of carbohydrate result in high levels of insulin. What is the effect of high levels of insulin on
lipid utilization?
protein metabolism?
Children suffering from kwashiorkor often have large distended bellies caused by water from the blood leaking into extracellular spaces. Suggest a biochemical basis for this condition.
Question 27.26
One for all, all for one. How is the metabolism of the liver coordinated with that of skeletal muscle during strenuous exercise?
Question 27.27
A little help, please? What is the advantage of converting pyruvate into lactate in skeletal muscle?
Question 27.28
Fuel choice. What is the major fuel for resting muscle? What is the major fuel for muscle under strenuous work conditions?
Question 27.29
Hefty reimbursement. Endurance athletes sometimes follow the exercise-
Question 27.30
Oxygen deficit. After light exercise, the oxygen consumed in recovery is approximately equal to the oxygen deficit, which is the amount of additional oxygen that would have been consumed had oxygen consumption reached steady state immediately. How is the oxygen consumed in recovery used?
Question 27.31
Excess post-
Question 27.32
Psychotropic effects. Ethanol is unusual in that it is freely soluble in both water and lipids. Thus, it has access to all regions of the highly vascularized brain. Although the molecular basis of ethanol action in the brain is not clear, ethanol evidently influences a number of neurotransmitter receptors and ion channels. Suggest a biochemical explanation for the diverse effects of ethanol.
826
Question 27.33
Fiber type. Skeletal muscle has several distinct fiber types. Type I is used primarily for aerobic activity, whereas type IIb is specialized for short, intense bursts of activity. How could you distinguish between these types of muscle fiber if you viewed them with an electron microscope?
Question 27.34
Tour de France. Cyclists in the Tour de France (more than 2000 miles in 3 weeks) require about 836,000 kJ (200,000 kcal) of energy, or 41,840 kJ (10,000 kcal) day−1 (a resting male requires 8368 kJ, or 2000 kcal, day−1).
With the assumptions that the energy yield of ATP is about 50.2 kJ (12 kcal) mol−1 and that ATP has a molecular weight of 503 g mol−1, how much ATP would be expended by a Tour de France cyclist?
Pure ATP can be purchased at a cost of approximately $150 per gram. How much would it cost to power a cyclist through the Tour de France if the ATP had to be purchased?
Question 27.35
Responding to stress. Why does it make good physiological sense that regular bouts of prolonged exercise will result in mitochondrial biogenesis?
Question 27.36
Burning fats. How does the activation of AMP-
Question 27.37
Saving protein. What metabolic and hormonal changes account for decreased gluconeogenesis during the first several weeks of starvation in humans?
Question 27.38
Did I do that!? Alcohol consumption on an empty stomach results in some interesting biochemical as well as embarrassing behavioral alterations. We will ignore the latter. Gluconeogenesis falls; there are increases in intracellular ratios of lactate to pyruvate, of glycerol 3-
Why does ethanol consumption result in the altered ratios?
Why does hypoglycemia and blood acidosis result in the hungry individual?
Why does the well-
fed person not experience hypoglycemia?
Question 27.39
Skip the candy bar. Humans can survive longer by total fasting than on a diet consisting entirely of small amounts of carbohydrates. What is going on?
Question 27.40
Too much of a good thing. What is the relation between fatty acid oxidation and insulin resistance in the muscle?
Question 27.41
Aneurin? Really? Why are the symptoms of beriberi similar to those of Wernicke–
Data Interpretation Problem
Question 27.42
Lactate threshold. The graph shows the relation between blood-
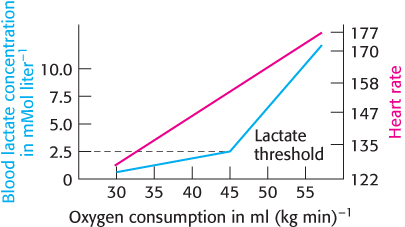
Why is some lactate produced even when exercise is moderate?
Biochemically, what is taking place when the lactate concentration begins to rise rapidly, a point called the lactate threshold?
Endurance athletes will sometimes measure blood-
lactate levels during training so that they know their lactate threshold. Then, during events, they will race just at or below their lactate threshold until the late stages of the race. Biochemically, why is this practice wise? Training can increase the lactate threshold. Explain.
Chapter Integration Problems
Question 27.43
Feeling the burn. Under certain circumstances, the respiratory quotient (RQ value) for an athlete exercising intensely can rise above one. How is this possible?
Question 27.44
So many channels. Like cable TV. Describe the role of ion channels in insulin secretion by the β cells of the pancreas.