PROBLEMS
PROBLEMS
Question 29.1
Complements. The sequence of part of an mRNA is
5′–AUGGGGAACAGCAAGAGUGGGGCCCUGUCCAAGGAG–
What is the sequence of the DNA coding strand? Of the DNA template strand?
Question 29.2
Checking for errors. Why is RNA synthesis not as carefully monitored for errors as is DNA synthesis?
Question 29.3
Speed is not of the essence. Why is it advantageous for DNA synthesis to be more rapid than RNA synthesis?
891
Question 29.4
Active sites. The overall structures of RNA polymerase and DNA polymerase are very different, yet their active sites show considerable similarities. What do the similarities suggest about the evolutionary relationship between these two important enzymes?
Question 29.5
Potent inhibitor. Heparin inhibits transcription by binding to RNA polymerase. What properties of heparin allow it to bind so effectively to RNA polymerase?
Question 29.6
A loose cannon. Sigma protein by itself does not bind to promoter sites. Predict the effect of a mutation enabling σ to bind to the −10 region in the absence of other subunits of RNA polymerase.
Question 29.7
Stuck sigma. What would be the likely effect of a mutation that prevents σ from dissociating from the RNA polymerase core?
Question 29.8
Transcription time. What is the minimum length of time required for the synthesis by E. coli polymerase of an mRNA encoding a 100-
Question 29.9
Rapid search. RNA polymerase finds promoter sites very rapidly. The observed rate constant for the binding of the RNA polymerase holoenzyme to promoter sequences is 1010 M−1s−1. The rate constant for two macromolecules encountering each other is typically 108 M−1s−1. Propose an explanation for the 100-
Question 29.10
Where to begin? Identify the likely transcription start site in the following DNA sequence:
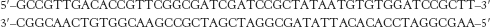
Question 29.11
Between bubbles. How far apart are transcription bubbles on E. coli genes that are being transcribed at a maximal rate?
Question 29.12
A revealing bubble. Consider the synthetic RNA–
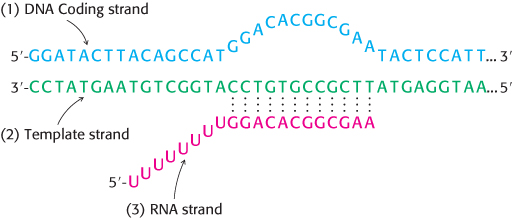
Suppose that strand 3 is labeled with 32P at its 5′ end and that polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is carried out under nondenaturing conditions. Predict the autoradiographic pattern for (i) strand 3 alone, (ii) strands 1 and 3, (iii) strands 2 and 3, (iv) strands 1, 2, and 3, and (v) strands 1, 2, and 3 and core RNA polymerase.
What is the likely effect of rifampicin on RNA synthesis in this system?
Heparin blocks elongation of the RNA primer if it is added to core RNA polymerase before the onset of transcription but not if added after transcription starts. Account for this difference.
Suppose that synthesis is carried out in the presence of ATP, CTP, and UTP. Compare the length of the longest product obtained with that expected when all four ribonucleoside triphosphates are present.
Question 29.13
Proofreading marks. The major products of proofreading by RNA polymerase are dinucleotides rather than mononucleotides. Why?
Question 29.14
Abortive cycling. Di-
Question 29.15
Polymerase inhibition. Cordycepin inhibits poly(A) synthesis at low concentrations and RNA synthesis at higher concentrations.
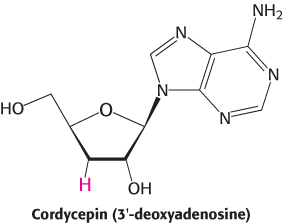
What is the basis of inhibition by cordycepin?
Why is poly(A) synthesis more sensitive than the synthesis of other RNAs to the presence of cordycepin?
Does cordycepin need to be modified to exert its effect?
Question 29.16
Alternative splicing. A gene contains eight sites where alternative splicing is possible. Assuming that the splicing pattern at each site is independent of that at all other sites, how many splicing products are possible?
Question 29.17
Supercoiling. Negative supercoiling of DNA favors the transcription of genes because it facilitates unwinding. However, not all promoter sites are stimulated by negative supercoiling. The promoter site for topoisomerase II itself is a noteworthy exception. Negative supercoiling decreases the rate of transcription of this gene. Propose a possible mechanism for this effect and suggest a reason why it may occur.
892
Question 29.18
An extra piece. In one type of mutation leading to a form of thalassemia, the mutation of a single base (G to A) generates a new 3′ splice site (blue in the illustration below) akin to the normal one (yellow) but farther upstream.
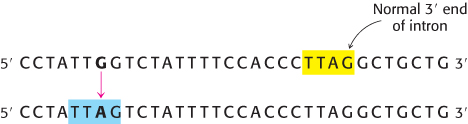
What is the amino acid sequence of the extra segment of protein synthesized in a thalassemic patient having a mutation leading to aberrant splicing? The reading frame after the splice site begins with TCT.
Question 29.19
A long-
Mechanism Problem
Question 29.20
RNA editing. Many uridine molecules are inserted into some mitochondrial mRNAs in trypanosomes. The uridine residues come from the poly(U) tail of a donor strand. Nucleoside triphosphates do not participate in this reaction. Propose a reaction mechanism that accounts for these findings. (Hint: Relate RNA editing to RNA splicing.)
Chapter Integration Problems
Question 29.21
Proteome complexity. What processes considered in this chapter make the proteome more complex than the genome? What processes might further enhance this complexity?
Question 29.22
Separation technique. Suggest a means by which you could separate mRNA from the other types of RNA in a eukaryotic cell.
Data Interpretation Problems
Question 29.23
Run-
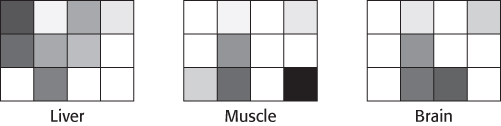
Why does the intensity of hybridization differ between genes?
What is the significance of the fact that some of the RNA molecules display different hybridization patterns in different tissues?
Some genes are expressed in all three tissues. What would you guess is the nature of these genes?
Suggest a reason why an initiation inhibitor was included in the reaction mixture.
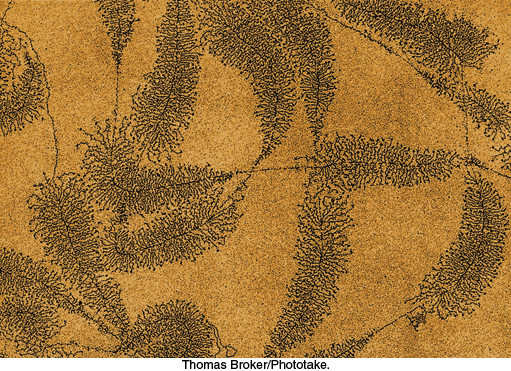
Question 29.24
Christmas trees. The adjoining autoradiograph depicts several bacterial genes undergoing transcription. Identify the DNA. What are the strands of increasing length? Where is the beginning of transcription? The end of transcription? On the page, what is the direction of RNA synthesis? What can you conclude about the number of enzymes participating in RNA synthesis on a given gene?