PROBLEMS
PROBLEMS
Question 36.1
Routes to discovery. For each of the following drugs, indicate whether the physiological effects of the drug were known before or after the target was identified.
Penicillin
Sildenafil (Viagra)
Rofecoxib (Vioxx)
Atorvastatin (Lipitor)
Aspirin
Indinavir (Crixivan)
Question 36.2
Lipinski’s rules. Which of the following compounds satisfy all of Lipinski’s rules? [Log(P) values are given in parentheses.]
Atenolol (0.23)
Sildenafil (3.18)
Indinavir (2.78)
1056
Question 36.3
Calculating log tables. Considerable effort has been expended to develop computer programs that can estimate log(P) values entirely on the basis of chemical structure. Why would such programs be useful?
Question 36.4
An ounce of prevention. Legislation has been proposed that would require that N-acetylcysteine be added to acetaminophen tablets. Speculate about the role of this additive.
Question 36.5
Clinical-
Question 36.6
Drug interactions. As noted in this chapter, coumadin can be a very dangerous drug because too much can cause uncontrolled bleeding. Persons taking coumadin must be careful about taking other drugs, particularly those that bind to albumin. Propose a mechanism for this drug–
Question 36.7
A bad combination. Explain why drugs that inhibit P450 enzymes may be particularly dangerous when used in combination with other medications.
Question 36.8
Mechanistically speaking. Name one advantage of a noncompetitive inhibitor as a potential drug compared with a competitive inhibitor.
Question 36.9
A helping hand. You have developed a drug that is capable of inhibiting the ABC transporter MDR. Suggest a possible application for this drug in cancer chemotherapy.
Question 36.10
Find the target. Trypanosomes are unicellular parasites that cause sleeping sickness. During one stage of their life cycle, these organisms live in the bloodstream and derive all of their energy from glycolysis, which takes place in a specialized organelle called a glycosome inside the parasite. Propose potential targets for treating sleeping sickness. What are some potential difficulties with your approach?
Question 36.11
Knowledge is power. How might genomic information be helpful for the effective use of imatinib mesylate (Gleevec) in cancer chemotherapy?
Question 36.12
Multiple targets, same goal. Sildenafil induces its physiological effects by increasing the intracellular concentrations of cGMP, leading to muscle relaxation. On the basis of the scheme shown in Figure 36.17, identify another approach for increasing cGMP levels with a small molecule.
Mechanism Problem
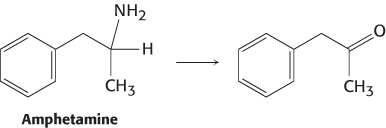
Question 36.13
Variations on a theme. The metabolism of amphetamine by cytochrome P450 enzymes results in the conversion shown here. Propose a mechanism and indicate any additional products.
Data Interpretation Problem
Question 36.14
HIV protease inhibitor design. Compound A is one of a series that were designed to be potent inhibitors of HIV protease.
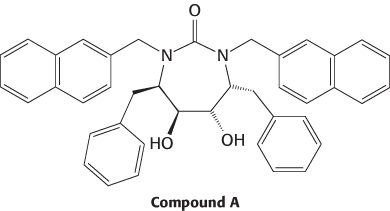
Compound A was tested by using two assays: (1) direct inhibition of HIV protease in vitro and (2) inhibition of viral RNA production in HIV-
|
Compound A (nM) |
HIV protease activity (arbitrary units) |
|---|---|
|
0 |
11.2 |
|
0.2 |
9.9 |
|
0.4 |
7.4 |
|
0.6 |
5.6 |
|
0.8 |
4.8 |
|
1 |
4.0 |
|
2 |
2.2 |
|
10 |
0.9 |
|
100 |
0.2 |
|
Compound A (nM) |
Viral RNA production (arbitrary units) |
|---|---|
|
0 |
760 |
|
1.0 |
740 |
|
2.0 |
380 |
|
3.0 |
280 |
|
4.0 |
180 |
|
5.0 |
100 |
|
10 |
30 |
|
50 |
20 |
Estimate the values for the KI of compound A in the protease-
Treating rats with the relatively high oral dose of 20 mg kg−1 results in a maximum concentration of compound A of 0.4 µM. On the basis of this value, do you expect compound A to be effective in preventing HIV replication when taken orally?