Chapter 11. Mendelian Genetics
Objectives
After completing this exercise, you should be able to:
- Define and distinguish between the following pairs of terms: homozygous and heterozygous individuals; dominant and recessive alleles; genotype and phenotype.
- Calculate the phenotypic ratio and genotypic ratio of generations by using Punnett squares.
- Predict the effect of pleiotropy, incomplete dominance, codominance and epistasis on inheritance.
- Describe how phenotype is determined by genotype.
Background
Genetics is the science of heredity. In genetics we study how different characters are inherited by the new generation from parents. Gregor Mendel is regarded as the father of genetics. He started his work on sweet pea plants in the 1850s and laid the foundation for the modern genetics studies. Before we proceed further and learn to solve genetics problems, please review the definitions of the following terms: genome, genes, genotype, phenotype, allele, trait, homozygous, heterozygous, homozygous, dominant, recessive.
Please complete the pre-lab activity to define various above mentioned terms.
Activity 1
Monohybrid Cross and Review Websites
In monohybrid crosses, inheritance of only one trait is studied.
Always write down the phenotype and genotype in your Punnett square. The dominant phenotype is designated with a capital letter and the recessive phenotype is given the lowercase letter. Understand that genotypes are always diploid (Ex. AA) while gametes are haploid (Ex. A).
Example Cross: Monohybrid cross with complete dominance
Yellow plants (Y) are dominant over white plants (y).
You cross a heterozygous yellow plant (female) with a white male. Use a Punnett square to determine the expected genotypic and phenotypic ratios for the offspring.
Yellow plant genotype: Yy White plant genotype: yy
Yellow plant gametes: Y, y and White plant gametes: y, y
(Always put a comma between gametes as they represent two independent entities.)
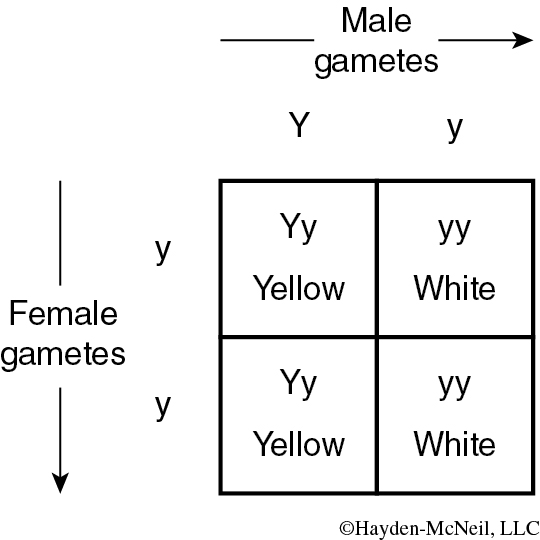
Genotypic ratio: 1Yy:1yy (Remember to always reduce, 2Yy:2yy reduces to 1:1 so write that down.)
Phenotypic ratio: 1 yellow:1 white.
Example Cross: Monohybrid cross with incomplete dominance
Red flowers (R) are dominant over white flowers (r). You cross a heterozygous plant (female) with a white male. Use a Punnett square to determine the expected genotypic and phenotypic ratios for the offspring. (Use the table above to figure out homo- and heterozygous.)
Plant genotype: Rr White plant genotype: rr
Plant gametes: R, r (Always put a comma between gametes.)
White plant gametes: r, r
Write down the phenotypes as you do the problem.
| Punnett Square |
r | r |
|---|---|---|
| R | Rr pink |
Rr pink |
| r | rr white |
rr white |
Genotypic ratio: 1 Rr: 1rr Phenotypic ratio: 1 pink : 1 white
Review Websites
http://wps.prenhall.com/wps/media/objects/1552/1589799/web_tut/20_02/20_02_01a.swf
Practice Problems
- Tall plants (T) are dominant over short plants (t). You cross a short plant (female) with a tall plant (male) that is heterozygous. Use a Punnett square to determine the expected genotypic and phenotypic ratios for the offspring.
| Tall plant genotype: | Short plant genotype: |
| Tall plant gametes: | Short plant gametes: |
(Please write all genotypes in the box.)
| Punnett Square | ||
Genotypic ratio:
Phenotypic ratio:
- Smooth seeds (S) are dominant over wrinkled seeds (s). You cross a plant that is homozygous for smooth seeds (male) with a plant that is heterozygous for smooth seeds (female). Use a Punnett square to determine the expected genotypic and phenotypic ratios for the offspring.
| Male plant’s genotype: | Female plant’s genotype: |
| Male plant’s gametes: | Female plant’s gametes: |
| Punnett Square | ||
Genotypic ratio:
Phenotypic ratio:
- Purple flowers (P) are dominant over white flowers (p) in pea plants. A plant that is heterozygous for purple flowers (male) is crossed with another plant that has white flowers (female). Use a Punnett square to determine the expected genotypic and phenotypic ratios for the offspring.
| Purple pea plant’s genotype: | White pea plant’s genotype: |
| Purple pea plant’s gametes: | White pea plant’s gametes: |
| Punnett Square | ||
Genotypic ratio:
Phenotypic ratio:
- In peas, tall plants (T) are dominant over short plants (t). You cross two heterozygous pea plants. Use a Punnett square to determine the expected genotypic and phenotypic ratios for the offspring.
| Male pea plant’s genotype : | Female pea plant’s genotype: |
| Male pea plant’s gametes : | Female pea plant’s gametes: |
| Punnett Square | ||
Genotypic ratio:
Phenotypic ratio:
- Purple flowers (P) are dominant over white flowers (p). If a pea plant is heterozygous for purple flowers, can any of this plant’s offspring have all purple flowers? Think about the different genotypes with which you can cross the heterozygote parent against: homozygous dominant, heterozygous, and homozygous recessive. Use three Punnett squares to show your work for each possible phenotype.
Unknown plant, list the 3 possible genotypes: (Use a different one for each cross; this would be “Mom” and there are 3 possible genotoypes.)
Heterozygous purple pea plant’s genotypes: (Use this in all the crosses-this would be “Dad,” he stays the same.)
| Punnett Square | ||
| Punnett Square | ||
| Punnett Square | ||
Which genotype will only give you purple flowers when crossed with the heterozygote?
Practice Problems (cont'd)
- Purple flowers (P) are dominant over white flowers (p). You cross two pea plants that are heterozygous for purple flowers. What are the chances that their offspring will have purple flowers…..white flowers? Express your answer as a percentage. Use a Punnett square to show your work.
Purple pea plant’s genotype:
The other purple pea plant’s genotype:
Purple pea plant’s gametes:
The other purple pea plant’s gametes:
| Punnett Square | ||
Probability that any of their offspring will have purple flowers: % and white flowers %
- Tall plants (T) are dominant over short (t) plants. You cross a tall plant with a short plant and out of 30 plants, 15 are tall and 15 are short. Give the PROBABLE genotypes of the parent tall plant, parent short plant, and offspring. You will need to use a Punnett square for each possible genotype of the tall parent.
Parent tall plant’s possible genotypes:
Parent short plant’s genotype:
Offspring genotype(s):
| Punnett Square | ||
Or
| Punnett Square | ||
Which cross gave you the 1:1 ratio of tall to short? Give me the genotype of the parent and offspring of that cross. You have just figured out the genotype of the unknown parent.
Genotype of Tall Parent: Genotypes of offspring:
-
It’s another boring day at Hotellgene Incorporated, but you’ve willingly come to work because genetics is your life, and besides you couldn’t let your boss down. You set to work crossing red and white beans as part of your experimenting. The beans that you are using are both homozygous for their respective traits. Thinking that this will be an easy cross, you write down in your lab book that the offspring will probably be all red. You assume that red is dominant and white is recessive. But after you do that cross you get some amazing results. Your results: all pink beans. Being the resourceful scientist that you are, you take the pink beans and cross them. As a result you get a phenotypic ratio of 1 red to 2 pink to 1 white. How are you going to explain these results to your boss, that the phenotypic ratio is not the expected 3:1?
This is because of incomplete dominance. The heterozygote is pink in color. This is only possible if red color is not 100% dominant over white.
-
Mrs. and Mr. Williams both have widow’s peaks (dominant). Their first child also has a widow’s peak, but their second child doesn’t. Mr. Williams accuses Mrs. Williams of being unfaithful to him. Is he necessarily justified? Why or why not? Work the genetics problem predicting the frequencies of the versions of this trait among their prospective children.
His accusations are not justified as they both could be heterozygous...
Activity 2
Dihybrid Problems
In dihybrid crosses inheritance of two traits is studied. These two traits under the study are assumed to be independently assorted.
- Wolves are sometimes observed to have black coats and blue eyes. Assume further that silver coat color (S) is dominant to black (s) and brown eyes (B) are dominant to blue (b). Suppose the alpha male and alpha female of a pack (these are the dominant individuals who do most of the breeding) are heterozygous for coat color and eye color. What will be the phenotypic ratio?
Male parent genotype: Female parent genotype:
Male gametes: Female gametes:
Punnett square: Write the genotype and phenotype in each square or points will be taken off. Note: Please do not use commas in your response, use a space instead.
| SB | Sb | sB | sb | |
| SB | ||||
| Sb | ||||
| sB | ||||
| sb |
Phenotype ratio of offspring: : : : (indicate colors of coat and eyes)
You don’t need to do the gentotypic ratio.
- In retrievers, coat color is determined by the interaction of two genes (pigment and deposition of pigment). This is called epistasis. Coat color can be black (B) or brown (b) and deposition of pigment into the hair shaft is deposited (E) or not deposited (e). If a retriever has the genotype where they have _ _ee, then they will have a yellow coat regardless of what color they inherit (ex: BBee or bbee gives a yellow coat). Calculate the phenotypic ratios of a cross between a male and female retrievers that are heterozygous for coat color and heterozygous for deposition of pigment.
Male parent genotype: Female parent genotype:
Male gametes : Female gametes :
Punnett square: Write the genotype and phenotype in each square or points will be taken off. Note: Please do not use commas in your response, use a space instead.
| BE | Be | bE | be | |
| BE | ||||
| Be | ||||
| bE | ||||
| be |
Phenotype ratio of offspring: : :
(Indicate colors of the coat.)
How did this compare to problem 1 above where there was no epistasis between two different traits?
- Show the cross between a “male” plant that is homozygous for red flowers and heterozygous for green seeds with a “female” plant that is heterozygous for red flowers and is heterozygous for green seeds. (Red flowers and green seeds are dominate.) Use “R” for red flowers and “r” for white flowers; “G” for green seeds and “g” for yellow seeds. What are the parents' genotypes? State the phenotypic ratios of the potential offspring.
| Male parent genotype: | Female parent genotype: |
| Male gametes: | Female gametes: |
Punnett square: Write the genotype and phenotype or points will be taken off. Note: Please do not use commas in your response, use a space instead.
| Punnett Square | ||||
Phenotype ratio of offspring:
Activity 3
Sex Linked Inheritance
In humans, we have 22 pairs (44) of regular chromosomes also known as autosomes and a pair (2) of sex- chromosomes. Sex chromosomes determine the sex of individuals. In humans the two sex chromosomes are called X and Y. If you have XX then you are a girl; but if you have XY then you are a boy!
Compared to the X chromosome, the Y chromosome is smaller in size (review the human karyotype in your textbook). The Y chromosome carries genes for the development of tests, whereas genes present on the X chromosome really do not help in sex determination. The X chromosome carries many housekeeping genes that are essential for both sexes. Thus when we talk about sex-linked genes we are talking about genes present on the sex chromosomes.
Since males carry only one copy of X chromosome, a recessive X-linked trait will influence the phenotype more often in males.
Several sex-linked and recessive disorders in humans include hemophilia, red-green color blindness, and Duchenne muscular dystrophy syndrome.
Please solve the following problems to understand sex-linked inheritance in humans.
Note: This a monohybrid cross but writing the alleles for sex-linked traits is different than what you did above. Now you will need to show that the allele is linked to the X chromosome by writing it as XH and Xh instead of simply H and h.
- Hemophilia is a sex-linked trait where XH gives normal blood clotting and is dominant to the hemophilia allele Xh. Males that are XHY are normal but males that are XhY are hemophiliacs. For women: XHXH are normal; XHXh are normal but carry the allele and are called carriers; XhXh have hemophilia.
a. Give the genotypes for:
1) Angelina with normal blood clotting whose father had hemophilia and
2) Brad whose father had hemophilia.
3) Please cross Angelina and Brad (answer box does not accept superscripts, please use normal letters).
Angelina’s genotype: Brad’s genotype:
Angelina’s gametes: Brad’s gametes:
b. What is the probability that a mating between these two individuals will produce a child, regardless of sex, that has hemophilia?
| A. |
| B. |
| C. |
| D. |
Probability of any of the children having hemophilia?
c. If this couple has a daughter, what is the probability that the daughter will be a carrier (carries a copy of the normal gene and hemophilia gene) of the hemophilia trait? What is the probability a daughter would have hemophilia?
Daughter is a carrier: % Daughters with hemophilia: %
d. If this couple has a son, what is the probability he will have hemophilia?
Son with hemophilia: %
- Mike is colorblind. His wife, Meg, is homozygous for the normal color vision allele. If they have eight children, how many of them would you expect to be colorblind? Using Punnett squares, derive and compare the genotypic and phenotypic ratios expected for the offspring of this marriage.
Genotypes for Meg and Mike are:
- Meg is homozygous for normal vision so XNXN
- Mike is colorblind so his genotype is XnY
(Answer box does not accept superscripts, please use normal letters.)
Meg's gametes: Mike's gametes:
Activity 4
Crosses Involving Blood Types (Codominance)
In humans the blood type is regulated by three alleles (A, B, and O). We observe four blood types namely: A, B, AB, and O in society. These 4 phenotypes arise from more than 4 genotypic combinations. Please look carefully the table below to understand this concept.
| Blood type (phenotype) | Genotype |
| A | AA or AO |
| B | BB or BO |
| AB | AB |
| O | OO |
Please solve the following problems related to human blood typing.
- It was suspected that two babies had been exchanged in a hospital. Mr. and Mrs. Brown received baby #1 and Mr. and Mrs. Green received baby #2. Blood typing tests on the parents and the babies showed the following:
| Mr. Brown: Type A | Mr. Green: Type AB |
| Mrs. Brown: Type O | Mrs. Green: Type O |
| Baby #1: Type A | Baby #2 Type O |
Complete the Punnett square for Mr. and Mrs. Green to determine whether the families received the right babies.
Did both the families get the right baby? Why?
- A woman has a daughter. There are three men whom she claims might have been the father of the child. The judge in the paternity court orders that all three men, the child, and the mother have blood tests. The results are: mother, Type A; Daughter, Type O; Man #1, Type AB; Man #2, Type B; Man #3, Type O. The mother claims that this proves that Man #3 must be the little girl’s father.
Is the mother correct? Why or why not?
