28a. Appropriate form and tense
This section offers a brief review of English verb forms and tenses. For additional help, see 27 and 46c.
Basic verb forms
Every main verb in English has five forms, which are used to create all of the verb tenses in Standard English. The following chart shows these forms for the regular verb help and the irregular verbs give and be. See 27a for a list of other common irregular verbs.
Basic verb forms
| regular verb help | irregular verb give | irregular verb be* | |
| base form | help | give | be |
| past tense | helped | gave | was, were |
| past participle | helped | given | been |
| present participle | helping | giving | being |
| -s form | helps | gives | is |
*Be also has the forms am and are, which are used in the present tense.
Verb tenses
Section 27f describes all the verb tenses in English, showing the forms of a regular verb, an irregular verb, and the verb be in each tense. The following chart provides more details about the tenses commonly used in the active voice in writing; the chart in 28b gives details about tenses commonly used in the passive voice.
Verb tenses commonly used in the active voice
For descriptions and examples of all verb tenses, see 27f. For verb tenses commonly used in the passive voice, see the chart in 28b.
Simple tensesFor general facts, states of being, habitual actions
| Simple present | Base form or -s form |
|
College students often study late at night. |
|
Water becomes steam at 100 degrees centigrade. |
|
We donate to a different charity each year. |
|
The train arrives tomorrow at 6:30 p.m. |
note: For uses of the present tense in writing about literature, see page 352.
| Simple past | Base form + -ed or -d or irregular form |
|
The storm destroyed their property. She drove to Montana three years ago. |
|
When I was young, I usually walked to school with my sister. |
| Simple future | will + base form |
|
I will exercise tomorrow. The snowfall will begin around midnight. |
Simple progressive formsFor continuing actions
| Present progressive | am, is, are + present participle |
|
The students are taking an exam in Room 105. The valet is parking the car. |
|
I am leaving tomorrow morning. |
| Past progressive | was, were + present participle |
|
They were swimming when the storm struck. |
|
We were going to drive to Florida for spring break, but the car broke down. |
note: Some verbs are not normally used in the progressive: appear, believe, belong, contain, have, hear, know, like, need, see, seem, taste, understand, and want.
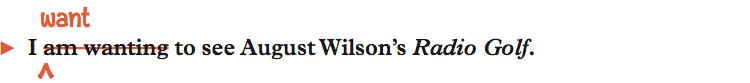
Perfect tensesFor actions that happened before another present or past time
| Present perfect | has, have + past participle |
|
I have loved cats since I was a child. Alicia has worked in Kenya for ten years. |
|
Stephen has visited Wales three times. |
| Past perfect | had + past participle |
|
She had just crossed the street when the runaway car crashed into the building. |
note: For more on the past perfect, see 27f. For uses of the past perfect in conditional sentences, see 28e.
Perfect progressive formsFor continuous past actions before another present or past time
| Present perfect progressive | has, have + been + present participle |
|
Yolanda has been trying to get a job in Boston for five years. |
| Past perfect progressive | had + been + present participle |
|
By the time I moved to Georgia, I had been supporting myself for five years. |