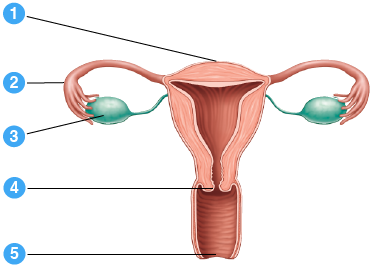
In which of the following female reproductive structures does oogenesis begin?
As is the case in spermatogenesis, oogenesis begins with diploid cells that multiply by mitosis. The diploid cells in oogenesis are called oogonia.
When does the process of oogenesis and the formation of oogonia begin in a female?
Meiosis begins in the ovaries while the female is still a fetus but stops at __________.
At this point, when the cell is arrested in prophase I of meiosis, what is it called?
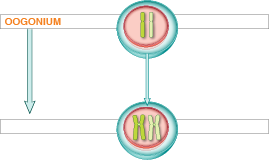

The cell is now called a primary oocyte. It is contained within a
structure known as the follicle inside of the ovary. The cells that
comprise the follicle will support and nurture the developing egg.

NEXT
At what point does the process of meiosis resume?
When meiosis resumes, the primary oocyte divides to form a large _______ and a smaller _______.


The next step in female gametogenesis is ovulation. What generally happens during ovulation?
During ovulation, generally a single follicle in one ovary ruptures, and the secondary oocyte and a few follicle cells are released into the Fallopian tube. Most of the follicle cells, however, remain in the ovary and form a transient endocrine structure called the corpus luteum.

NEXT
At what point does the process of meiosis resume?
After fertilization, the secondary oocyte completes meiosis to form a large ________ and a smaller ________.


Why does oogenesis involve two asymmetrical divisions that ultimately result in a large ovum that receives most of the cytoplasm and smaller polar bodies that receive almost no cytoplasm?
Hormones regulate the timing of both the ovarian and menstrual cycles. It is essential that these two cycles be linked so that the uterus is prepared to receive and nurture the embryo if fertilization does occur. Which of the following events marks the first day of the menstrual cycle?
When circulating estrogen levels are low, the anterior pituitary gland produces increasing amounts of which of the following hormones?
What is the effect of increasing levels of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)?
Which hormone is produced and released by the developing follicles?
High levels of estrogen trigger the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary. What is the effect of the LH surge?
After ovulation, the follicle cells remaining in the ovary form the corpus luteum. Which hormone(s) are produced by the corpus luteum?
What is the primary effect of high levels of progesterone?