True or False:
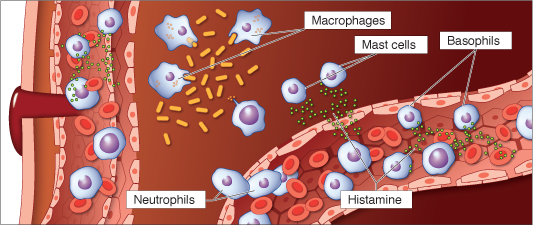
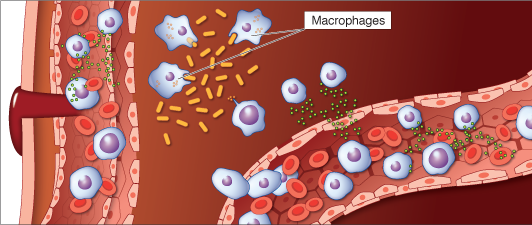
Histamine causes uninjured blood vessels to dilate, and the increased blood flow resulting from this dilation is directly responsible for ALL of the symptoms of the inflammatory response: redness, heat, swelling, and pain.
Histamine causes uninjured blood vessels to dilate, and the increased blood flow resulting from this dilation is directly responsible for ALL of the symptoms of the inflammatory response: redness, heat, swelling, and pain.