Air is taken into the body here.

Photo credit: Woman in tank top: Fancy/Veer/Corbis
The two entry points for air join together here (also known as the “throat”).
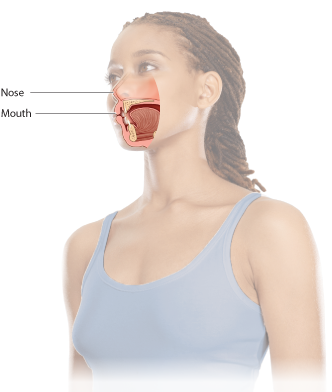
Photo credit: Woman in tank top: Fancy/Veer/Corbis
After air passes through the throat, it passes through this structure, often referred to as the “voice box.”

Photo credit: Woman in tank top: Fancy/Veer/Corbis
Often called the “windpipe,” this long tube takes air into the chest cavity.

Photo credit: Woman in tank top: Fancy/Veer/Corbis
These organs are characterized by highly branched, moist respiratory surfaces where gases are exchanged between air and blood. They resemble stretchy, elastic bags.
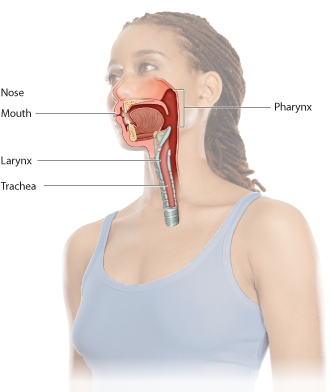
Photo credit: Woman in tank top: Fancy/Veer/Corbis
These branching tubes carry air into each lung and then branch into even smaller tubes.
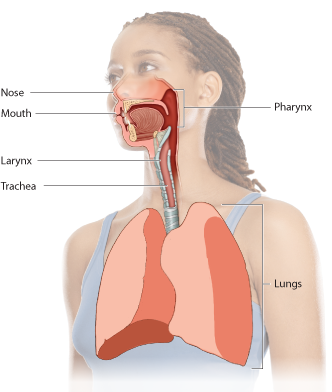
Photo credit: Woman in tank top: Fancy/Veer/Corbis
These small, fingerlike tubes branch and spread out into the lungs.
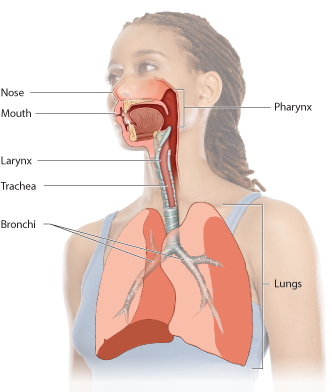
Photo credit: Woman in tank top: Fancy/Veer/Corbis
These tiny, elastic sacs are where air meets the blood vessels.

Photo credit: Woman in tank top: Fancy/Veer/Corbis
These tiny, elastic sacs are where air meets the blood vessels.
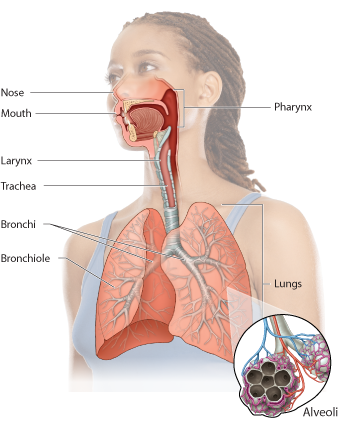
Photo credit: Woman in tank top: Fancy/Veer/Corbis
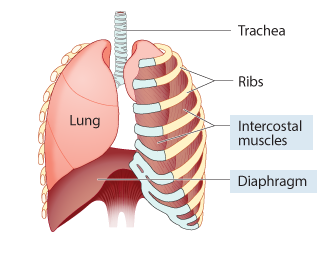
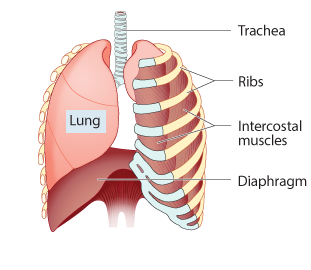
During inhalation:
The diaphragm and intercostal muscles ______.
relax
contract
Inhalation
Exhalation
During inhalation:
The diaphragm is pulled ______,
and the rib cage ______.
lower, expands
higher, contracts

Inhalation
Exhalation
During inhalation:
Air is ______.
sucked into the lungs
pushed out of the lungs
Inhalation
Exhalation
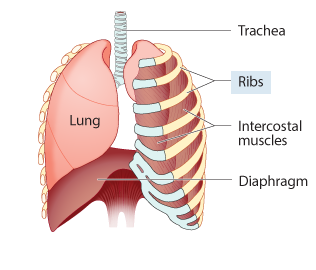
During exhalation:
The diaphragm and intercostal muscles ______.
relax
contract

Inhalation
Exhalation
During exhalation:
The rib cage and chest cavity ______.
expand
contract
Inhalation
Exhalation
During exhalation:
Air is ______.
pushed out of the lungs
sucked into the lungs

Inhalation
Exhalation