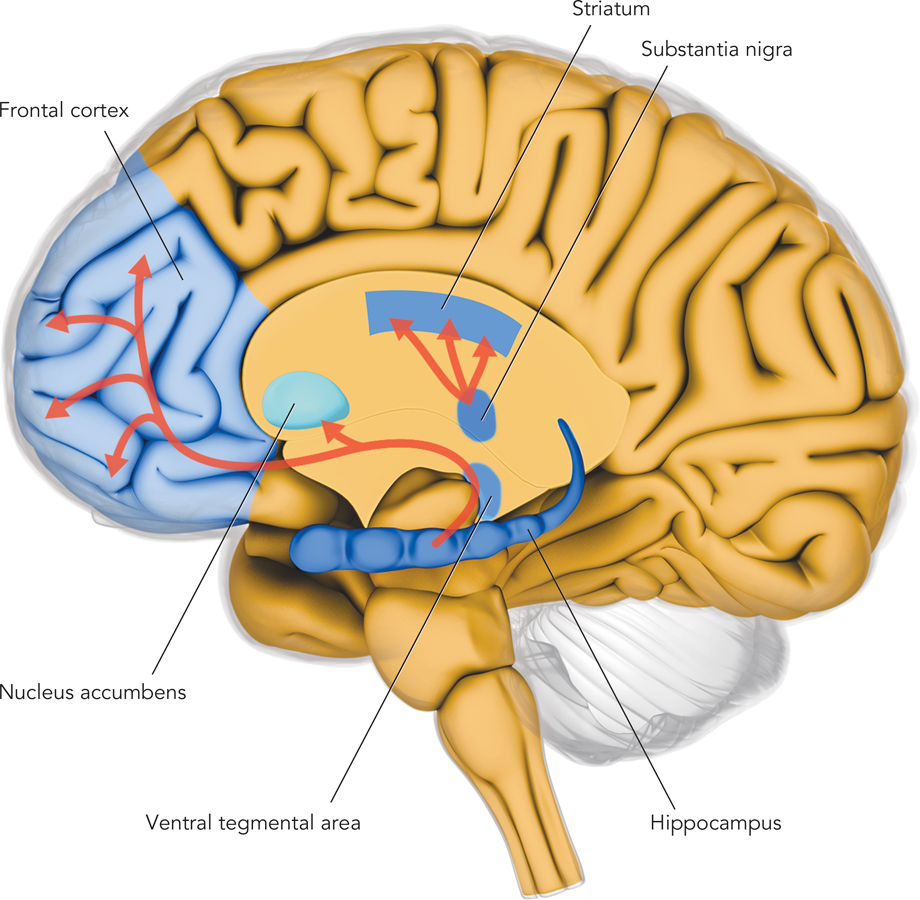
figure 16.1 Dopamine pathways The neurotransmitter dopamine affects activity in the brain, thereby affecting psychological experience and behavior. Its effects are widespread, thanks to dopamine pathways, which are routes within the brain that transfer dopamine from one brain region to another. The pathways take dopamine to a set of lower-level brain regions that control motor movement and the experience of pleasure in activities; these include the nucleus accumbens, ventral tegmental area, striatum, substantia nigra, and hippocampus. Pathways also lead to the frontal cortex, which is involved in self-reflection and the planning of goal-directed behavior. According to the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia, abnormal levels of dopamine are responsible for schizophrenia symptoms.