FIGURE 5
The Kinked Demand Curve Model of Oligopoly The kinked demand curve model of oligopoly shows why oligopoly prices appear stable. The model assumes that if the firm raised its price, competitors will not react and raise their prices, but if the firm lowers its price, other firms will lower theirs in response. These reactions create a “kink” in the firm’s demand curve at point e, and a discontinuity in the MR curve equal to the distance between points a and b. This discontinuity permits marginal costs to vary from MC0 to MC1 before the firm will change its price.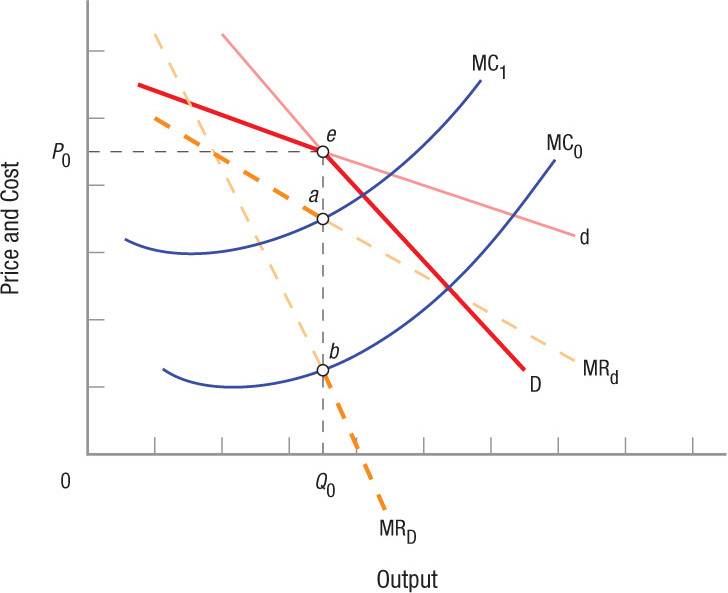
[Leave] [Close]