FIGURE 1
Individual Supply of Labor When wages are W1, this individual will work l1 hours, but when the wage rate rises to W2, her willingness to work rises to l2. Over these two wage rates she is substituting work for leisure. Once the wage rises above W2, the income effect begins to dominate, since she now has sufficient income that leisure is now more important and her labor supply curve is backward bending.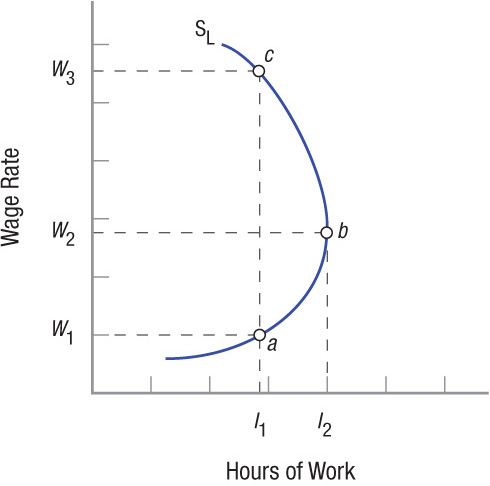
[Leave] [Close]