FIGURE 5
Job Crowding and a Dual Labor Market Segregated markets can lead to significant wage differentials between men and women. Without discrimination, equilibrium wages will be W0 for everyone, with total employment at M0 + F0. If, however, there is some form of discrimination in male-dominated jobs, the supply of labor to that segment will decline to S1, wages will rise to W1, and employment will fall to M1 (point a). Those women who are excluded from jobs in this sector will have to move to available jobs in the female-dominated sector, thus increasing the labor supplied for these jobs to S2, raising employment to F2, but reducing wages to W2 (point b). The result is a wage differential equal to W1 − W2.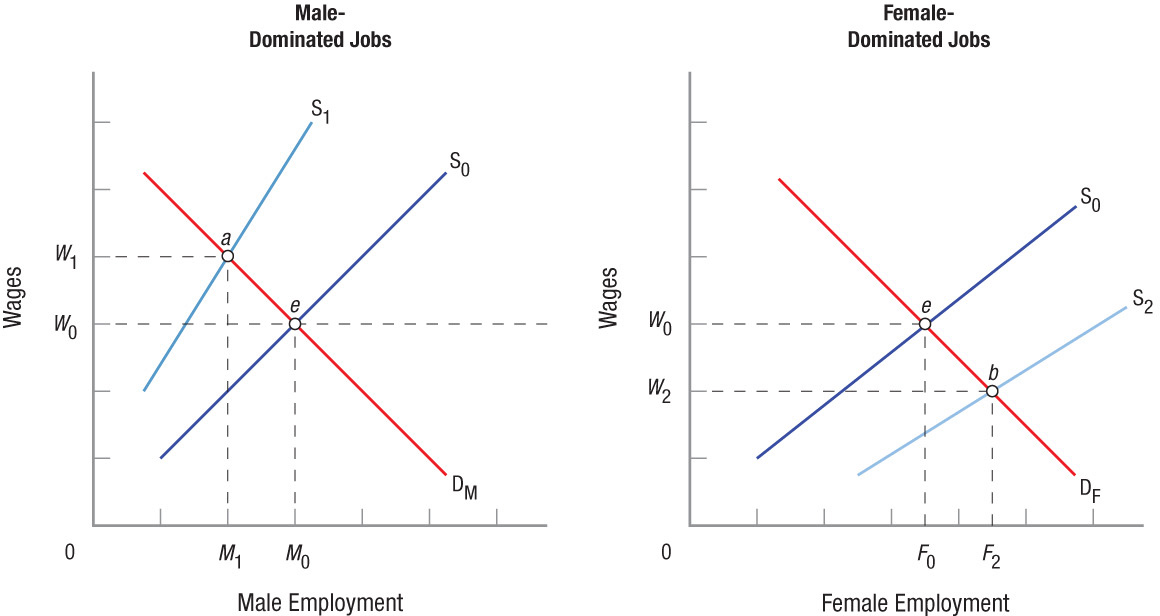
[Leave] [Close]