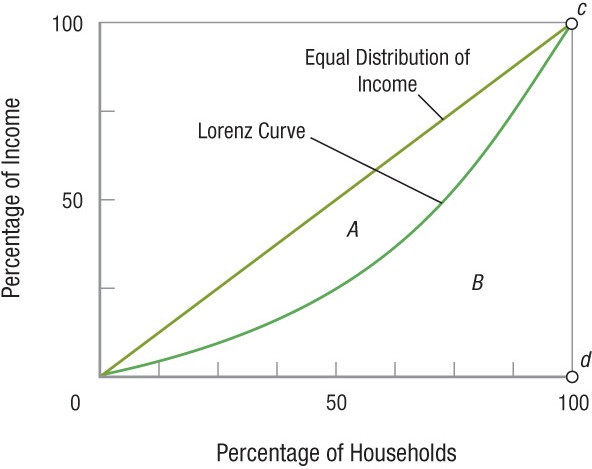
The Gini Coefficient The Gini coefficient is a precise method of measuring the position of the Lorenz curve. It is defined as the ratio of the area between the Lorenz curve and the equal distribution line, and the total area below the equal distribution line. Thus, the Gini coefficient is equal to the ratio between area A and area (A + B). If distribution were equal, area A would be zero, and the Gini coefficient would equal zero. If distribution were as unequal as possible, area B would disappear, thus the Gini coefficient would be 1.