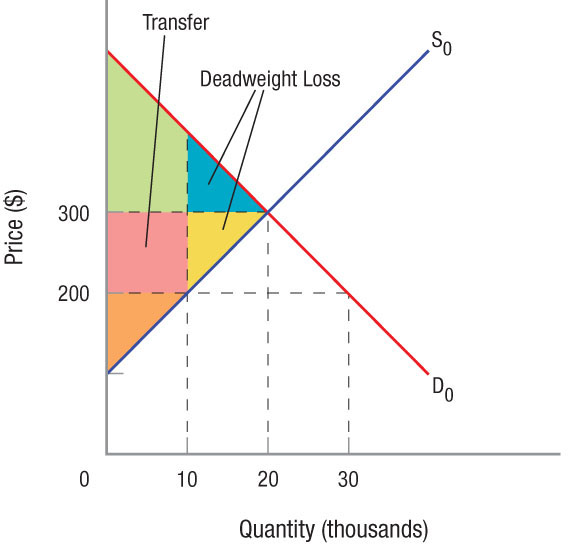
Consumer and Producer Surplus When Prices are Below Equilibrium Compared to the equilibrium price, a price of $200 causes some producers to not sell the product, resulting in a loss of producer surplus equal to the yellow area. Further, producers who still sell the product earn $100 less than before, causing an additional loss of producer surplus equal to the pink area. Consumers, meanwhile, lose consumer surplus equal to the blue area resulting from the shortage of units, but receive additional consumer surplus equal to the pink area as a result of the lower price for those lucky enough to find units for sale. Once again, deadweight loss is the blue and yellow areas, and the pink area is surplus transferred.