Chapter Summary
Chapter Summary
Section 1: Monopolistic Competition
A monopolistically competitive industry has the following characteristics:
- Large number of firms with insignificant market share.
- No barriers to entry and exit.
- Products sold by firms are similar but differentiated (has a brand).
- Limited market power.
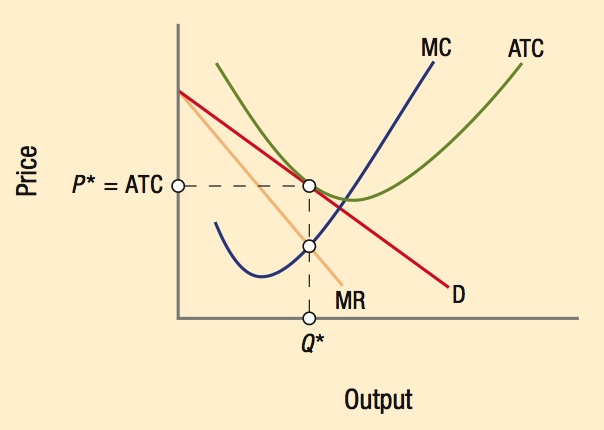
Short-run profit maximization for a monopolistically competitive industry looks identical to a monopoly. In the long run, however, the demand curve is tangent to the average total cost curve, signaling zero economic profit.
Because of product differentiation, a firm’s demand curve is downward sloping. However, it is highly elastic due to the competitive nature of the industry.

Types of Product Differentiation
Location
Quality
Style, Design, and Features
Advertising
Section 2: Oligopoly

Oligopoly industries are controlled by a few large firms. Barriers to entry are significant, the product is less differentiated than in monopolistically competitive industries, and pricing decisions by one firm directly impact other firms (mutual interdependence). Oligopoly firms possess market power but not as much as a monopoly.
Cartels are agreements to restrict output to push prices higher, but are inherently unstable because cheating is profitable.
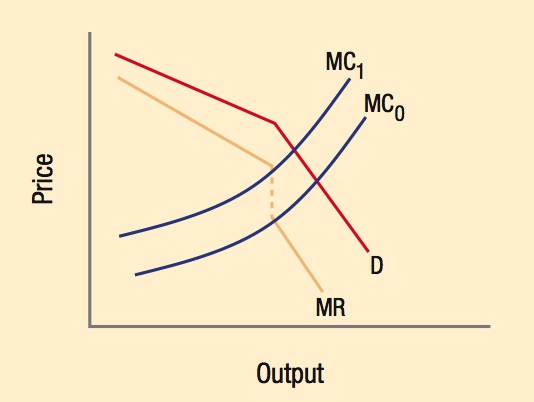
A kinked demand curve occurs because firms are reluctant to match price increases but not price decreases. The kink creates a discontinuity in the marginal revenue curve, allowing marginal cost to vary (from MC0 to MC1) while prices remain stable.
Section 3: Game Theory
Game theory is the study of strategic decision making when multiple players each act in their own interests.

Components of a Game
Players
Information
Strategy choices
Outcomes and payoffs
Nash equilibrium is an outcome that results from all players responding optimally to all other players’ actions to maximize their expected payoffs. In a Nash equilibrium, no player wishes to deviate unilaterally from that outcome.
Solving for a Nash equilibrium requires analyzing a game table for best responses to the other player’s possible actions.
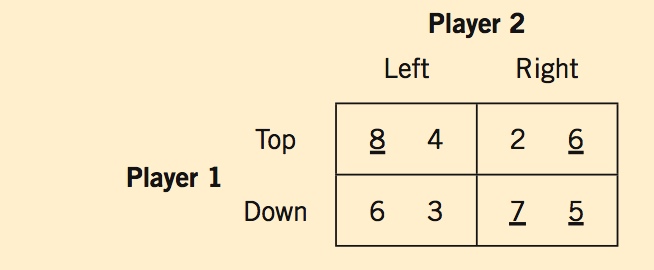
Player 1’s best response to “Left” is “Top” = 8.
Player 1’s best response to “Right” is “Down” = 7.
Player 2’s best response to “Top” is “Right” = 6.
Player 2’s best response to “Down” is “Right” = 5.
One Nash equilibrium = “Down”, “Right” = (7, 5).
Section 4: Applications of Game Theory
A Prisoner’s Dilemma occurs when optimal noncooperative play results in an outcome that is inferior to another for both players.
Ways to Overcome the Prisoner’s Dilemma
Collusion: This is illegal in most cases, although international cartels exist, such as the OPEC oil cartel and the De Beers diamond cartel. Also, free trade agreements are a legal form of cooperation between countries.
Tacit collusion: Occurs when one player takes the lead, and everyone else follows. This strategy is more effective when games are repeated, allowing for the possibility of retaliation should other players not cooperate.

Trigger Strategies Used in Repeated Games
Grim trigger: When one player defects, the other refuses to cooperate again (no forgiveness).
Trembling hand trigger: Players forgive certain instances of defection as “mistakes” before retaliation is taken.
Tit-for-tat trigger: Essentially an eye-for-an-eye: If one player defects, the other player punishes this player until cooperation resumes.
Chicken games occur when opposing players have an incentive to maintain a tough stance; however, if neither player refuses to back down, the worst outcome for both players occurs.