Chapter Summary
Chapter Summary
Section 1: Competitive Labor Supply
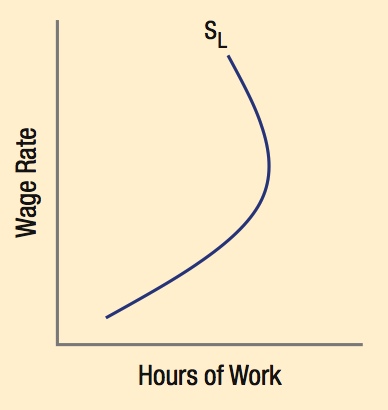

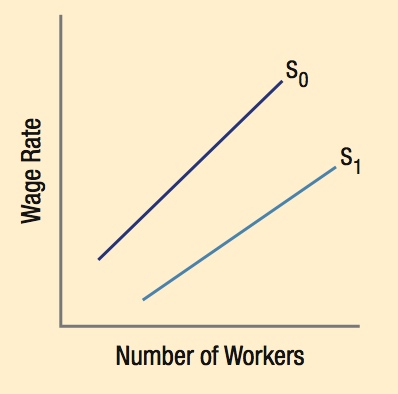
Work Versus Leisure: The Relationship Between Wages and Hours Worked
- Substitution effect: higher wages lead to more hours worked, and vice versa
- Income effect: higher wages lead to fewer hours worked, and vice versa
A strong income effect means that a worker chooses to work fewer hours as wages increase to pursue other activities (such as studying). This leads to a backward-bending individual labor supply curve.
Factors That Change Labor Supply
- Demographic changes (population growth, immigration, labor force participation)
- Nonmoney aspects of jobs
- Wages in alternative jobs
- Nonwage income
Market labor supply curves are upward sloping and can shift due to the factors listed above.
Section 2: Competitive Labor Demand
A firm’s demand for labor is a derived demand: It depends on the productivity of labor and the demand for the good or service workers produce.
Factors That Change Labor Demand
- Change in product demand (affecting MR)
- Changes in productivity (affecting MPPL)
- Changes in prices of other inputs
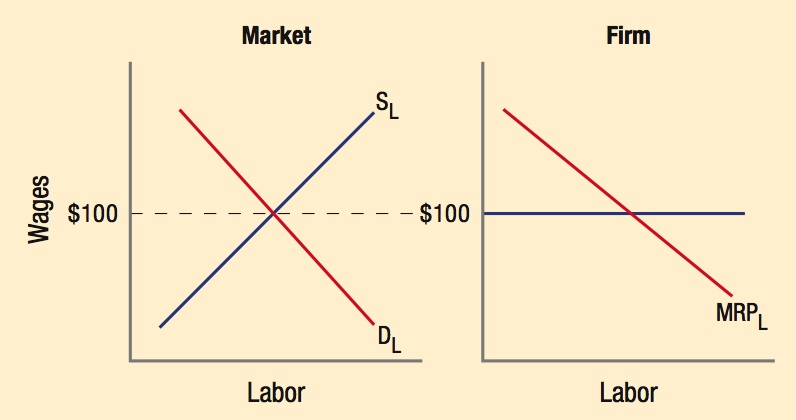
In a competitive labor market, wages are determined by the intersection of labor supply and labor demand. For an individual firm, they take wages as given (firms are price takers) and hire workers until its MRP equals the wage.
Marginal Revenue Product (MRP) = MPPL × MR
- MPPL is the marginal physical product.
- MR is the marginal revenue from the product.
- MRP is the value provided by the last worker.
- Firms hire workers until MRP = wage.
Section 3: Economic Discrimination
Economic discrimination occurs whenever workers of equal ability and productivity are paid different wages or otherwise discriminated against because of their:
- race or color
- religion
- gender
- age
- national origin
- sexual orientation
- disability

Laws Banning Labor Discrimination
- On gender: Equal Pay Act of 1963
- On race/ethnicity: Civil Rights Act of 1964
- On age: Age Discrimination in Employment Act of 1967
- On disabilities: Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990
Firms That Discriminate Must Pay More for Labor
- The supply of “preferred” workers decreases in a segmented market, increasing their wage.
- “Nonpreferred” workers enter a different market, increasing the labor supply and decreasing their wage.
- Firms that hire “nonpreferred” workers enjoy greater profits from a lower cost of labor.
Section 4: Labor Unions and Collective Bargaining
Labor unions are legal associations of employees formed to bargain collectively with employers over the terms and conditions of employment. They use:
- Strikes
- Threats of strikes
- Other tactics
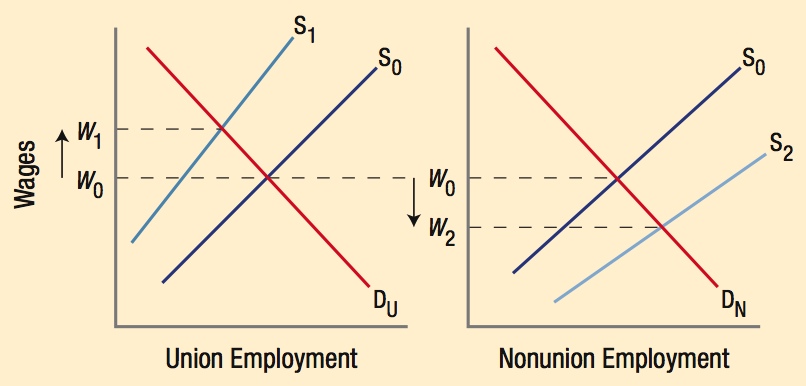
Unions restrict labor supply, shifting the labor supply to the left, raising wages. Those not in the union are forced to find nonunion jobs, increasing the labor supply in those markets and lowering wages, creating a wage gap of W1 − W2.
Major Laws Affecting Unions in the United States
- Wagner Act (National Labor Relations Act): protected union workers and their rights
- Taft-Hartley Act: Placed rules on unions to prevent them from becoming too powerful
Section 5: The Changing World of Work
Changes in the U.S. Labor Force
- Two-earner families: more women in labor force
- Immigration growth filling low-wage jobs
- Increase in flex-time workers: workers that are able to set their own work hours
Significant Changes in Careers in the Past 50 Years
- Shift from manufacturing to service industries
- Significant growth in international trade and foreign direct investment
- The introduction of the Internet, which has transformed the manufacturing process